httpd
HTTPd is a software program that usually runs in the background, as a process, and plays the role of a server in a client–server model using the HTTP and/or HTTPS network protocol(s).
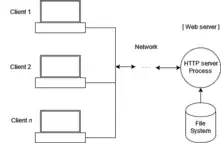
PC clients communicating via network with an HTTPd process serving static content only.
The process waits for the incoming client requests and for each request it answers by replying with requested information, including the sending of the requested web resource, or with an HTTP error message.
HTTPd stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol daemon.
It usually is the main software part of an HTTP server better known as a web server.[1]
Some commonly used implementations are:
- Apache HTTP Server
- BusyBox httpd
- CERN HTTPd HTTP server
- Cherokee HTTP server
- Hiawatha HTTP server with reverse proxy functionality
- Lighttpd HTTP server
- NCSA HTTPd HTTP server
- Nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server
- OpenBSD's httpd (since OpenBSD 5.6)
- Thttpd HTTP server
- TUX web server aka kHTTPd
References
- "Server and supporting programs". Apache: HTTPd server project. 2021. Retrieved 2021-11-19.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.