Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire, or simply Ethiopia, also known as "Abyssinia" by foreigners, was an empire in Africa. It used to include modern day Ethiopia and Eritrea. When it was biggest, it controlled some parts of Egypt, Sudan, Yemen, and Saudi Arabia.
Ethiopian Empire | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1270–1974 1936–1941: Government-in-exile | |||||||||||||||||||
| Motto: ኢትዮጵያ ታበፅዕ እደዊሃ ሃበ እግዚአብሐር Ityopia tabetsih edewiha habe Igziabiher (English: "Ethiopia Stretches Her Hands unto God") ("Ethiopia Stretches Her Hands unto God") (Psalm 68:31) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Anthem: "ኢትዮጵያ ሆይ ደስ ይበልሽ" (English: "Ethiopia, be happy") | |||||||||||||||||||
 The Ethiopian Empire boundaries in 1952 | |||||||||||||||||||
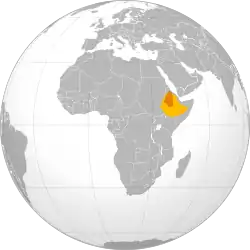 The location of the Ethiopian Empire during the reign of Yohannes IV (dark orange) compared with modern day Ethiopia (orange) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Unspecified (1270–1635) Gondar (1635–1855) Magdala (1855–1868) Mekelle (1871–1885) Addis Ababa (1886–1974) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Ge’ez Amharic Oromo Tigrinya | ||||||||||||||||||
| Religion |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Endonym: Ethiopian Exonym: Abyssinian (in non-native sources, derived from the Arabic name for the general region "Al-Habash" and the most widely prominent pan-ethnic group the Habesha) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Absolute monarchy[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||||||||
• 1270 (first) | Yekuno Amlak[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
• 1930–1974 (last) | Haile Selassie | ||||||||||||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||||||||||||
• 1909–1927 (first) | Habte Giyorgis | ||||||||||||||||||
• 1974 (last) | Mikael Imru | ||||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Parliament[3] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Senate | |||||||||||||||||||
| Chamber of Deputies | |||||||||||||||||||
Predecessor States
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages to Cold War | ||||||||||||||||||
• Empire established | 1270 | ||||||||||||||||||
• Ethiopian-Adal war | 1529–1543 | ||||||||||||||||||
• Italian Eritrea | 1890 | ||||||||||||||||||
• Constitution adopted | 16 July 1931 | ||||||||||||||||||
• Conquered by Italy (annexed to Italian East Africa) | 3 October 1935 | ||||||||||||||||||
• Sovereignty restored | 5 May 1941 | ||||||||||||||||||
• Admitted to the UN | 13 November 1945 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 12 September 1974 | |||||||||||||||||||
• Monarchy abolished | 21 March 1975[4][5][6][7] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1950 | 1,221,900 km2 (471,800 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1974 | 1,221,900 km2 (471,800 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||||
• 1950 | 19,575,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
• 1974 | 35,074,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Currency |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||||||
Abyssinia was mentioned in Egyptian records in 980 BC. Its king made the country Christian in the 4th century. The Solomonid dynasty ruled from 1270 to 1974 A.D., when it was overthrown by communists. At the time of its overthrow, it was the longest-lasting government in the world and one of the only two nations that did not get colonized in Africa.
In other languages
Ethiopian Empire:
- Ge'ez Script: የኢትዮጵያ ንጉሠ ነገሥት መንግሥተ, Mängəstä Ityop'p'ya
Ethiopia:
References
- Nathaniel T. Kenney (1965). "Ethiopian Adventure". National Geographic. 127: 555.
- Negash, Tekeste (2006). "The Zagwe Period and the Zenith of Urban Culture in Ethiopia, Ca. 930-1270 Ad". Africa: Rivista Trimestrale di Studi e Documentazione dell'istituto Italiano per l'Africa e l'Oriente. 61 (1): 120–137. JSTOR 40761842.
- Constitution of Ethiopia, 4 November 1955, Article 76 (source: Constitutions of Nations: Volume I, Africa by Amos Jenkins Peaslee)
- "Ethiopia Ends 3,000 Year Monarchy". Milwaukee Sentinel. 22 March 1975. p. 3.
- "Ethiopia ends old monarchy". The Day. 22 March 1975. p. 7.
- Henc van Maarseveen; Ger van der Tang (1978). Written Constitutions: A Computerized Comparative Study. Brill. p. 47.
- "Ethiopia". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 1987.

Abyssinia in 1896

Map
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
.svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)