Centripetal force
Centripetal force is an accelerating force that acts on any body that revolves around a centre. This force contributes to keeping the body in rotation. This force is always directed towards the centre.
_a.jpg.webp)
The opposite force (by Isaac Newton's third law of motion) is called centrifugal force. This is the force that acts on the body in a direction away from the centre, which contributes to making the body try to fly away. When you hold a rope with a heavy object attached to it, and rotate it around, the rope becomes tight and keeps the body from flying away. This is caused by centripetal force.
An example is a roller coaster which uses centripetal force to accelerate the carts so they will keep going in a circular motion. Even if an object changes direction but maintains at a constant speed it still counts as acceleration.
Geometric proof for uniform circular motion
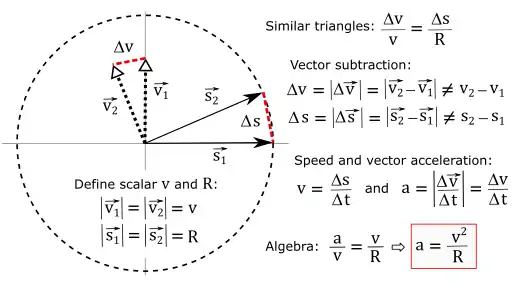
In the figure to the right we define the displacement vector to represent motion in a circle. The magnitude of is denoted as and represents the radius of the particle's orbit.