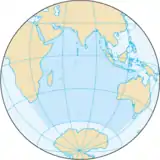
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the ocean surrounded by Asia to the north, Australia and the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Southern Ocean to the south, and Africa and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. It is named for the river Indus and Ancient India on its north shore. The Bay of Bengal, the Arabian Sea, the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea are all parts of this ocean.
| Earth's oceans (World Ocean) |
|---|
|
|
The deepest point in the Indian Ocean is in the Java Trench near the Sunda Islands in the east, 7500 m (25,344 feet) deep. The average depth is 3,890 m (12,762 ft). The Indian Ocean is the third largest ocean, 28,350,000 square miles in size. The majority is in the southern hemisphere.
Other websites
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Indian Ocean.
- Maps of the indian Ocean
- Océan Indien in easy French
- NOAA In-situ Ocean Data Viewer Archived 2011-12-24 at the Wayback Machine Plot and download ocean observations
- The Indian Ocean in World History: Educational Website Interactive resource from the Sultan Qaboos Cultural Center
- The Regional Tuna Tagging Project-Indian Ocean with details of the importance of Tuna in the Indian Ocean.. Archived 2017-09-11 at the Wayback Machine
- Detailed maps of the Indian Ocean
- The Indian Ocean Trade: A Classroom Simulation Archived 2011-09-25 at the Wayback Machine
- CIA - The World Factbook, Oceans: Indian Ocean Archived 2014-05-09 at the Wayback Machine
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.