Cabinet of the Netherlands
The cabinet of the Netherlands (Dutch: Nederlands kabinet) is the main executive body of the Netherlands. The latest cabinet of the Netherlands is the Fourth Rutte cabinet,[1] which has been in power since 10 January 2022, until 7 July 2023. It is headed by Prime Minister Mark Rutte.[2]
| Part of the Politics series |
![Azure, billetty Or a lion with a coronet Or armed and langued Gules holding in his dexter paw a sword Argent hilted Or and in the sinister paw seven arrows Argent pointed and bound together Or. [The seven arrows stand for the seven provinces of the Union of Utrecht.] The shield is crowned with the (Dutch) royal crown and supported by two lions Or armed and langued gules. They stand on a scroll Azure with the text (Or) "Je Maintiendrai" (French for "I will maintain".)](../I/State_coat_of_arms_of_the_Netherlands.svg.png.webp) |
|---|
|
|
Composition and role

The cabinet consists of the ministers and state secretaries. The cabinet is led by the Prime Minister. There are between twelve and sixteen Ministers, most of whom are also heads of specific government ministries, although there are often some ministers without portfolio who have areas of responsibility inside one or more ministries. For instance there has for some time been a minister for development cooperation, who works within the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Most ministries also have a state secretary who is responsible for part of the relevant portfolio. State secretaries (such as that of Trade and Development Cooperation) are given the right to call themselves "Minister" in other countries and be treated as such for protocolary purposes, while not having any of the domestic rights given specifically to Ministers. Most significantly, state secretaries are not members of the Council of Ministers.
The policy of a cabinet is coordinated by the Council of Ministers, in which all ministers, including ministers without portfolio, take part. The Council initiates laws and policy. State secretaries do not attend the Council of Ministers unless invited, and even then they have no voting rights in the Council. The Council meets every Friday in the Trêveszaal (the Room of Treaties) in the Binnenhof. Meetings are chaired by the Prime Minister, or an acting Prime Minister if necessary. The Council makes decisions in a collegial manner; all ministers, including the Prime Minister, are (theoretically) equal. Behind the closed doors of the Trêveszaal, ministers can freely debate proposed decisions and express their opinion on any aspect of cabinet policy. Once a decision is made by the Council, all individual members are bound by it and are obliged to support it publicly. A member of Cabinet who is not prepared to publicly support a decision of the Council is obliged to step down. Typically, a good deal of effort is put into reaching relative consensus on any decision. A process of voting within the Council does exist, but is hardly ever used.
Together with the King, the Council of Ministers forms the Government, which makes all the major decisions. In practice, the King does not participate in the daily decision-making of government, although he is kept up to date by weekly meetings with the Prime Minister. The Dutch constitution does not speak of cabinet, but instead only of the Council of Ministers and Government.
The ministers, individually and collectively (as cabinet), are responsible to the States-General for government policy and must enjoy its confidence. It is not possible for a minister to be a member of parliament. Ministers or state secretaries who are no longer supported by a parliamentary majority are also expected by convention to step down. In contrast to the Westminster system, Dutch ministers may not simultaneously also be members of the States-General, although members of the States-General can be appointed as ministers, whereupon their seats become vacant.
An important question is whether the relationship between the cabinet and parliament should be dualistic or monistic. That is, whether ministers and leaders of governing parliamentary parties should prepare important political decisions. According to the dualistic position, members of parliament of governing parties should function independently of the Cabinet. The monistic position, by contrast, is that the Cabinet plays an important role in proposing legislation and policy.
The Cabinet typically meets at least once a week and is presided by the Prime Minister.[3]
Formation
After a general election held generally every four years, or if a cabinet resigns during a parliamentary term, the process of cabinet formation starts. Because of the multi-party system of the Netherlands, no single party has had a majority in parliament since 1900, and formation of a coalition of two or often three parties is always necessary. This is a time-consuming process. The entire procedure is regulated by tradition and convention, with only the final appointment process specified by law.
Initially, the Dutch Monarch has secret individual meetings with the presidents of the Senate and House of Representatives, and the Vice-President of the Council of State. Next the Monarch has a meeting with the leader of each parliamentary party in the House of Representatives. This is followed by appointing an informateur who explores the options of a new cabinet. The informateur is often a relative outsider and a veteran politician, who has retired from active politics, perhaps a member of the Senate or Raad van State, though by convention has a background in the largest party in the House of Representatives. The Monarch may appoint multiple informateurs, with backgrounds in other parties. The informateur is given a specific task by the King or Queen regnant, often to "seek a coalition of parties with programmatic agreement and a majority in parliament." The informateur has one-on-one meetings with the leaders of the parliamentary parties, and chairs sessions of negotiations between the chairs of parliamentary parties as they compromise in order to achieve agreement. If negotiations break down, a new informateur is appointed and the information process begins afresh.
Once an informateur is successful, the Monarch appoints the formateur,[4] conventionally the leader of the largest party in the prospective coalition and the likely Prime Minister. the formateur leads any remaining negotiations between those parties willing to cooperate to form a cabinet. Often, these negotiations cover the details of the program of policies, the composition of the Cabinet, and the division of Ministerial portfolios.
If the formateur is successful, the Monarch appoints all ministers and state secretaries individually by Royal Decision (Koninklijk Besluit). Each Minister privately swears an oath of loyalty to the Constitution. After this the entire Council of Ministers and the King or Queen regnant are photographed on the stairs of the palace Huis ten Bosch during the bordes scene. The new cabinet then proposes its plans to parliament.
Between the dissolution of the States-General before general elections and the appointment of a new Cabinet, the incumbent Cabinet is termed demissionair, that is, a caretaker government limiting itself to urgent and pressing matters and traditionally not taking any controversial decisions. If a Cabinet falls during a parliamentary term because one of the coalition partners withdraws its support, the coalition partner in question may leave. This does not result in a demissionair Cabinet, unless the Prime Minister is granted a dissolution of the States-General. Instead, the remaining parties in the governing coalition form a rompkabinet ("rump cabinet"). If the parties do not between them control a majority of the House of Representatives, the Cabinet continues as a minority government.
The formation is often considered as important as or even more important than the elections themselves. Because of the importance of negotiations, which can lead to policies that no party has promoted during the election, cabinet formations are sometimes seen as undemocratic. Recently it was attempted to make the process more democratic, with the formateur and informateur accounting for their actions before both the House of Representatives and the Dutch Monarch. Another source of discontent with this process is the role of the monarch in it.
Incumbent Cabinet
| Title | Minister | Term of office | Party | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image | Name | Start | End | |||
| Prime Minister |  |
Mark Rutte | 14 October 2010[lower-roman 1] | Incumbent | VVD | |
| First Deputy Prime Minister | .jpg.webp) |
Sigrid Kaag | 10 January 2022 | 8 January 2024[lower-roman 2] | D66 | |
.jpg.webp) |
Rob Jetten | 8 January 2024 | Incumbent | |||
| Second Deputy Prime Minister | .jpg.webp) |
Wopke Hoekstra | 10 January 2022 | 1 September 2023[lower-roman 2] | CDA | |
 |
Karien van Gennip | 5 September 2023 | Incumbent | |||
| Third Deputy Prime Minister | .jpg.webp) |
Carola Schouten | 26 October 2017[lower-roman 1] | Incumbent | CU | |
| Title | Minister | Term of office | Party | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image | Name | Start | End | |||
| Minister of General Affairs |  |
Mark Rutte | 14 October 2010[lower-roman 1] | Incumbent | VVD | |
| Minister of Finance | .jpg.webp) |
Sigrid Kaag | 10 January 2022 | 8 January 2024[lower-roman 2] | D66 | |
.jpg.webp) |
Rob Jetten (ad interim)[lower-roman 3] | 8 January 2024 | 12 January 2024 | |||
.jpg.webp) |
Steven van Weyenberg | 12 January 2024 | Incumbent | |||
| Minister of Foreign Affairs | .jpg.webp) |
Wopke Hoekstra | 10 January 2022 | 1 September 2023[lower-roman 2] | CDA | |
_A_(cropped).jpg.webp) |
Liesje Schreinemacher (ad interim) | 1 September 2023 | 5 September 2023 | VVD | ||
.jpg.webp) |
Hanke Bruins Slot | 5 September 2023 | Incumbent | CDA | ||
| Minister of Justice and Security |  |
Dilan Yeşilgöz-Zegerius | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | VVD | |
| Minister of the Interior and Kingdom Relations | .jpg.webp) |
Hanke Bruins Slot | 10 January 2022 | 5 September 2023[lower-roman 4] | CDA | |
 |
Hugo de Jonge | 5 September 2023 | Incumbent | |||
| Minister of Education, Culture and Science |  |
Robbert Dijkgraaf | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | D66 | |
| Minister of Defence | .jpg.webp) |
Kajsa Ollongren | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | D66 | |
| Minister of Infrastructure and Water Management | .jpg.webp) |
Mark Harbers | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | VVD | |
| Minister of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy | _(cropped).jpg.webp) |
Micky Adriaansens | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | VVD | |
| Minister of Agriculture, Nature and Food Quality | Henk Staghouwer | 10 January 2022 | 5 September 2022[lower-roman 2] | CU | ||
.jpg.webp) |
Carola Schouten (ad interim) | 5 September 2022 | 4 October 2022 | |||
.jpg.webp) |
Piet Adema | 4 October 2022 | Incumbent | |||
| Minister of Social Affairs and Employment |  |
Karien van Gennip | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | CDA | |
| Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport | .jpg.webp) |
Ernst Kuipers | 10 January 2022 | 10 January 2024[lower-roman 2] | D66 | |
.png.webp) |
Conny Helder | 10 January 2024 | Incumbent | VVD | ||
| Ministry | Title | Minister | Term of office | Party | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image | Name | Start | End | ||||
| Social Affairs and Employment | Minister for Poverty Policy, Participation and Pensions | .jpg.webp) |
Carola Schouten | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | CU | |
| Foreign Affairs | Minister for Foreign Trade and Development Cooperation | _A_(cropped).jpg.webp) |
Liesje Schreinemacher | 10 January 2022 | 4 December 2023[lower-roman 5] | VVD | |
.jpg.webp) |
Geoffrey van Leeuwen (acting) | 4 December 2023 | 15 April 2024 | ||||
_A_(cropped).jpg.webp) |
Liesje Schreinemacher | 15 April 2024 | Incumbent | ||||
| Justice and Security | Minister for Legal Protection | .jpg.webp) |
Franc Weerwind | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | D66 | |
| Interior and Kingdom Relations | Minister for Housing and Spatial Planning |  |
Hugo de Jonge | 10 January 2022 | 5 September 2023[lower-roman 6] | CDA | |
| Education, Culture and Science | Minister for Primary and Secondary Education | .png.webp) |
Dennis Wiersma | 10 January 2022 | 22 June 2023[lower-roman 2] | VVD | |
.jpg.webp) |
Mariëlle Paul | 21 July 2023 | Incumbent | ||||
| Economic Affairs and Climate Policy | Minister for Climate and Energy Policy | .jpg.webp) |
Rob Jetten | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | D66 | |
| Agriculture, Nature and Food Quality | Minister for Nature and Nitrogen Policy | .png.webp) |
Christianne van der Wal | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | VVD | |
| Health, Welfare and Sport | Minister for Long-term Care and Sport | .png.webp) |
Conny Helder | 10 January 2022 | 10 January 2024[lower-roman 7] | VVD | |
| Minister for Medical Care | .jpg.webp) |
Pia Dijkstra | 2 February 2024 | Incumbent | D66 | ||
| Ministry | Title | State secretary | Term of office | Party | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image | Name | Start | End | ||||
| Justice and Security | State Secretary for Justice and Security[lower-roman 8] | .png.webp) |
Eric van der Burg | 10 January 2022 | 28 October 2023[lower-roman 9] | VVD | |
.png.webp) |
Christophe van der Maat (acting) | 30 October 2022 | 24 November 2023 | ||||
.png.webp) |
Eric van der Burg | 24 November 2023 | Incumbent | ||||
| Interior and Kingdom Relations | State Secretary for Kingdom Relations and Digitalisation[lower-roman 10] | .jpg.webp) |
Alexandra van Huffelen | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | D66 | |
| Education, Culture and Science | State Secretary for Culture and Media | .jpg.webp) |
Gunay Uslu | 10 January 2022 | 1 December 2023[lower-roman 2] | D66 | |
.jpg.webp) |
Steven van Weyenberg | 6 December 2023 | 12 January 2024[lower-roman 11] | ||||
.jpg.webp) |
Fleur Gräper | 12 December 2024 | Incumbent | ||||
| Finance | State Secretary for Tax Affairs and the Tax Administration |  |
Marnix van Rij | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | CDA | |
| State Secretary for Benefits and Customs | .png.webp) |
Aukje de Vries | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | VVD | ||
| Defence | State Secretary for Defence | .png.webp) |
Christophe van der Maat | 10 January 2022 | 30 October 2022[lower-roman 12] | VVD | |
| 24 November 2023 | Incumbent | ||||||
| Infrastructure and Water Management | State Secretary for Infrastructure and Water Management[lower-roman 13] |  |
Vivianne Heijnen | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | CDA | |
| Economic Affairs and Climate Policy | State Secretary for the Extractive Industries | .jpg.webp) |
Hans Vijlbrief | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | D66 | |
| Health, Welfare and Sport | State Secretary for Health, Welfare and Sport | .jpg.webp) |
Maarten van Ooijen | 10 January 2022 | Incumbent | CU | |
- Retained this position from the previous cabinet.
- Resigned from this position.
- Tasks were de facto delegated to State Secretary Marnix van Rij.
- Appointed as Minister of Foreign Affairs.
- Took maternity leave.
- Appointed as Minister of the Interior and Kingdom Relations.
- Appointed as Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport.
- Allowed to use the title "Minister for Migration" while on foreign business.
- Took an extended medical leave of absence.
- Allowed to use the title "Minister for Digitalisation" while on foreign business.
- Appointed as Minister of Finance.
- Appointed as acting State Secretary for Justice and Security.
- Allowed to use the title "Minister for the Environment" while on foreign business.
Ministries
There are now twelve ministries, all with their own Minister, there are also several Ministers without portfolio and in some ministries there is a State Secretary next to the Minister. The number of Ministers and State Secretaries and the division of their tasks may vary somewhat from one cabinet to another. The ministries are:
| Ministries | Responsibilities | Agencies / Independent Agencies |
Minister | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ministry of General Affairs (Dutch: Ministerie van Algemene Zaken) |
AZ | Government policy • Planning • Information • Dutch royal house |
• Government Information Service • Scientific Council for Government Policy • Cabinet Office • Review Committee on the Intelligence and Security Services |
Mark Rutte as Prime Minister and Minister of General Affairs |
| Ministry of the Interior and Kingdom Relations (Dutch: Ministerie van Binnenlandse Zaken en Koninkrijksrelaties) |
BZK | Domestic policy • Civil service • Public administration • Elections • Local governments • Intelligence • Kingdom Relations |
• Safety Board • General Intelligence and Security Service • PKIoverheid |
Hugo de Jonge as Minister of the Interior and Kingdom Relations |
| Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Dutch: Ministerie van Buitenlandse Zaken) |
BZ | Foreign relations • Foreign policy • International development • International trade • European Union • NATO • Benelux • Diaspora |
• Diplomatic Service • Center for the Promotion of Imports |
Hanke Bruins Slot as Minister of Foreign Affairs |
| Ministry of Finance (Dutch: Ministerie van Financiën) |
FIN | Economic policy • Monetary policy • Fiscal policy • Tax policy • Incomes policy • Financial market • Regulations • Government budget |
• Tax and Customs Administration • Fiscal Information and Investigation Service • Authority for the Financial Markets |
Rob Jetten as Minister of Finance |
| Ministry of Justice and Security (Dutch: Ministerie van Justitie en Veiligheid) |
J&V | Justice system • Law enforcement • Public security • Emergency management • Counter-terrorism • Immigration policy • Legal aid • Drug policy • Incarcerations |
• National Police Corps • Public Prosecution Service • National Coordinator for Security and Counterterrorism • Forensic Institute • Immigration and Naturalisation Service • Custodial Institutions Agency |
Dilan Yeşilgöz-Zegerius as Minister of Justice and Security |
| Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy (Dutch: Ministerie van Economische Zaken en Klimaat) |
EZK | Commercial policy • Energy policy • Environmental policy • Climate change policy • Renewable energy policy • Nuclear energy policy Industrial policy • Investment policy • Technology policy • Mining • Trade • Space policy • Natural resource • Tourism |
• Foreign Investment Agency • Space Office • Bureau for Economic Policy Analysis • Department of Nuclear Safety, Security and Safeguards • Patent Office • Central Agency for Statistics • Environmental Assessment Agency |
Micky Adriaansens as Minister of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy |
| Ministry of Defence (Dutch: Ministerie van Defensie) |
DEF | Armed forces • Military policy • National security • Veterans Affairs • Military police • Defence diplomacy • Humanitarian aid |
• Army • Navy • Air Force • Marechaussee • Coastguard • Military Intelligence and Security Service |
Kajsa Ollongren as Minister of Defence |
| Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport (Dutch: Ministerie van Volksgezondheid, Welzijn en Sport) |
VWS | Health care • Health policy • Health insurance • Pharmaceutical policy • Vaccination policy • Welfare • Biomedical sciences • Sport |
• Institute for Public Health and the Environment • Health Care Inspectorate |
Ernst Kuipers as Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport |
| Ministry of Social Affairs and Employment (Dutch: Ministerie van Sociale Zaken en Werkgelegenheid) |
SZW | Social policy • Employment • Labour economics • Occupational safety and health • Social security • Consumer protection • Trade unions • Trade associations • Emancipation |
• Social and Economic Council • Inspectorate SZW |
Karien van Gennip as Minister of Social Affairs and Employment |
| Ministry of Education, Culture and Science (Dutch: Ministerie van Onderwijs, Cultuur en Wetenschap) |
OCW | Education policy • Cultural policy • Science policy • Knowledge policy • Research • Innovation • Art • Gender equality • Communication • Media |
• Public Broadcasting Agency • National Archives • National Library • Equal Treatment Commission |
Robbert Dijkgraaf as Minister of Education, Culture and Science |
| Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management (Dutch: Ministerie van Infrastructuur en Waterstaat) |
I&W | Transport • Aviation • Housing policy • Public works • Spatial planning • Land management • Water Management |
• Rijkswaterstaat • Driving License and Certificates Agency • Meteorological Institute |
Mark Harbers as Minister of Infrastructure and Water Management |
| Ministry of Agriculture, Nature and Food Quality (Dutch: Ministerie van Landbouw, Natuur en Voedselkwaliteit) |
LNV | Agricultural policy • Food policy • Food safety • Fisheries • Natural conservation • Forestry • Animal welfare |
• Food and Consumer Product Safety Authority | Piet Adema as Minister of Agriculture, Nature and Food Quality |
History
The first real cabinet was formed in 1848 after a constitution was adopted which limited the power of the King and introduced the principle of ministerial responsibility to parliament. Until 1888 cabinets lacked a real coordinating role, and instead ministers were focused on their own department. After 1888 cabinets became more political.
Of the thirty coalition governments since World War II, only three excluded the largest party (all three times PvdA) and the largest number of parties in a coalition was 5 (in 1971 and 1973). After that, the three major Christian-democratic parties merged into CDA, and 2- or 3-party coalitions became standard.
Since 1945 there have been thirty cabinets, which were headed by 15 Prime Ministers. Willem Drees and Jan Peter Balkenende both chaired the most cabinets (four) and Ruud Lubbers served as Prime Minister the longest (between 1982 and 1994). The second Rutte cabinet was the longest lasting cabinet since World War II (1,816 days); only the cabinet led by Theo Heemskerk sat longer (2025 days). The first Balkenende cabinet is the shortest lasting normal cabinet since World War II (87 days); only the fifth cabinet of Hendrikus Colijn lasted shorter (10 days).
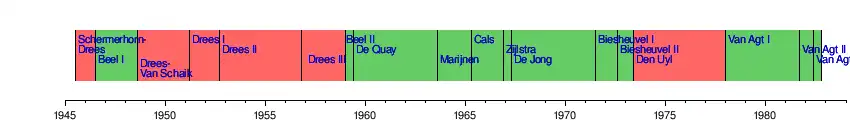
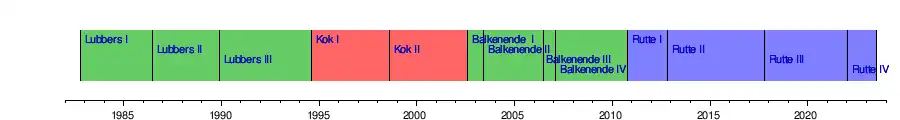
Council of Ministers of the Kingdom
The Cabinet of the Netherlands also takes responsibility for day-to-day affairs in the Kingdom of the Netherlands, which is distinct from the Netherlands, as it also includes the constituent countries of Aruba, Curaçao and Sint-Maarten. If affairs are decided which are of vital importance of the Kingdom as a whole, the Council of Ministers of the Netherlands is joined by a Minister Plenipotentiary for Aruba, Curaçao and Sint-Maarten to form the Council of Ministers of the Kingdom.
Types
There are different types of cabinets:
- A demissionary cabinet (demissionair kabinet) is a caretaker government during the election campaign and the formation of a new cabinet.
- An extra-parliamentary cabinet (extraparlementair kabinet) not based on a parliamentary majority. The last extra-parliamentary cabinet was the Den Uyl cabinet. It consisted of members of the three progressive parties (the social democratic PvdA, the social liberal D66, and the progressive Christian PPR) and progressive members from the Christian democratic ARP and KVP. It is contrasted with a parliamentary cabinet, which does have an explicit majority in parliament.
- A rump cabinet (rompkabinet) is the continuation of a Dutch cabinet when it has lost a coalition partner, typically a form of minority government, where the cabinet has not become demissionary, but seeks support from a majority of parliament to finish the work that was already introduced by the cabinet to the parliament. Normally the Dutch Monarch will call for dissolution of parliament somewhat later, since the basis behind the coalition agreement is gone.
- A broad basis cabinet (brede basiskabinet) is an oversized coalition or national cabinet. Between 1945 and 1959, several cabinets have included more parties than were necessary for a parliamentary majority. The first one of which was the Schermerhorn cabinet. Other parties were included to give the cabinet and its far-reaching proposals, like the formation of a welfare state, a broad basis in parliament and society. The core of these cabinets were formed by the social democratic PvdA and the catholic KVP, the Roman/Red alliance which by themselves had a large majority in parliament.
See also
- List of cabinets of the Netherlands
References
- Zaken, Ministerie van Algemene (2022-01-07). "Government - Government.nl". www.government.nl. Retrieved 2022-03-18.
- Zaken, Ministerie van Algemene (2015-04-17). "Members of the government - Government - Government.nl". www.government.nl. Retrieved 2022-03-18.
- Zaken, Ministerie van Algemene (2014-02-20). "How the Dutch Cabinet works - Government - Government.nl". www.government.nl. Retrieved 2022-03-18.
- Zaken, Ministerie van Algemene (2017-12-12). "Forming a new government - Government - Government.nl". www.government.nl. Retrieved 2022-03-18.