Provinces of Korea
Korea has had administrative districts that can be considered provinces since the 7th century. These divisions were initially called ju (Korean: 주; Hanja: 州) in Unified Silla and Later Baekje, and there were nine in total. After Goryeo conquered these states in the 10th century, twelve divisions called mok (목; 牧) were established, although they were reorganized into ten do (도; 道) in the 11th century.
After Joseon's conquest of Goryeo, it reorganized the peninsula into eight do in 1413. The provincial boundaries closely reflected major regional and dialect boundaries, and are still often referred to in Korean today simply as the Eight Provinces. In 1895, as part of the Gabo Reform, the country was redivided into 23 districts (Bu; 부; 府), which were replaced a year later by thirteen new provinces. The thirteen provinces of 1896 included three of the original eight provinces, with the five remaining original provinces divided into north and south halves (Bukdo (북도; 北道) and Namdo (남도; 南道) respectively). The thirteen provinces remained unchanged throughout the Japanese colonial period.
With the liberation of Korea in 1945, the Korean peninsula was divided into North Korea and South Korea, with the dividing line established along the 38th parallel. As a result, three provinces—Hwanghae, Gyeonggi, and Gangwon (Kangwŏn)—were divided into North Korea and South Korea today. The special cities of Seoul (South Korea) and P'yŏngyang (North Korea) were formed in 1946. Between 1946 and 1954, five new provinces were created: Jeju in South Korea, and North and South Hwanghae, Chagang, and Ryanggang in North Korea. Since 1954, provincial boundaries in both the North and South have remained unchanged but new cities and special administrative regions have been created.
Provinces of Unified Silla
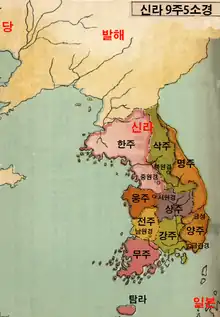
The Korean peninsula was mostly unified for the first time by the state Silla in the 7th century.[1] Silla's capital was Geumseong (now Gyeongju).[2] It had five sub-capitals (소경; 小京; sogyeong) at Geumgwan-gyeong (금관경, now Gimhae), Namwon-gyeong (남원경, Namwon), Seowon-gyeong (서원경, Cheongju), Jungwon-gyeong (중원경, Chungju), and Bugwon-gyeong (북원경, Wonju).[3]
The country was divided into nine provinces (주; ju): three in the pre-660 territory of Silla, and three each in the territories of the former kingdoms Baekje and Goguryeo.[4]
| Province | Hangul | Hanja | Capital | Modern equivalent | Former kingdom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yangju | 양주 | 良州 | Yangju | Eastern Gyeongsang | Silla |
| Gangju | 강주 | 康州 | Gangju | Western South Gyeongsang | |
| Sangju | 상주 | 尙州 | Sangju | Western North Gyeongsang | |
| Muju | 무주 | 武州 | Muju | South Jeolla | Baekje |
| Jeonju | 전주 | 全州 | Jeonju | North Jeolla | |
| Ungju | 웅주 | 熊州 | Gongju | South Chungcheong | |
| Hanju | 한주 | 漢州 | Hanju | North Chungcheong, Gyeonggi, Hwanghae | Goguryeo |
| Sakju | 삭주 | 朔州 | Sakju | Western Gangwon | |
| Myeongju | 명주 | 溟州 | Myeongju | Eastern Gangwon |
Provinces of Goryeo
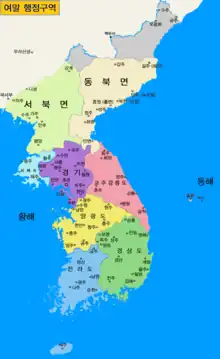
Goryeo was established in the 10th century, and had its capital at Gaegyeong (now Kaesong). It conquered Silla and Later Baekje, and also conquered parts of the former territory of Goguryeo.[5] Goryeo had three subcapitals: Donggyeong (now Gyeongju), Namgyeong (now Seoul), and Seogyeong (now Pyongyang).[6]
Goryeo reorganized its provinces several times. Originally, the country had one royal district (기내; 畿內; ginae) around Gaegyeong and twelve administrative districts (목; 牧; mok).[7] In 995, the twelve districts were redivided into ten provinces (도; 道; do).[8] In 1005,[8] the ten provinces were again redivided, this time into five provinces and two frontier districts (계; 界; gye). Gyojudo later became its own province after 1178, making it six provinces and two frontier districts.
| Provinces (pre-995)[7] | Provinces (995–1005)[8] | Provinces (post-1005)[9] |
Modern equivalent | Silla equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yangju-mok (揚州牧) | Gwannae-do | Seohae-do (西海道,서해도) | Hwanghae | Hanju |
| Hwangju-mok (黃州牧) | North Hwanghae | |||
| Haeju-mok (海州牧) | South Hwanghae | |||
| Gwangju-mok (廣州牧) | Yanggwang-do(楊廣道,양광도) | Gyeonggi | ||
| Chungju-mok (忠州牧) | Jungwon-do | North Chungcheong | ||
| Cheongju-mok | Ungju | |||
| Gongju-mok | Hanam-do | South Chungcheong | ||
| Jeonju-mok (全州牧) | Gangnam-do | Jeolla-do(전라도) | Jeonbuk | Jeonju |
| Naju-mok | Haeyang-do(해양도) | South Jeolla | Muju | |
| Seungju-mok | ||||
| Sangju-mok | Yeongnam-do | Gyeongsang-do(경상도) | North Gyeongsang | Sangju |
| Jinju-mok | Sannam-do | Western South Gyeongsang | Gangju | |
| Yeongdong-do | Eastern South Gyeongsang | Yangju | ||
| — | Sakbang-do | Gyoju-do(교주도,交州道),also known as gyoju gangneungdo(交州江陵道,교주강릉도)[lower-alpha 1] | Gangwon | Sakju |
| — | Donggye(東界,동계),also known as Dongbukmyeon(東北面,동북면) | Myeongju | ||
| — | Paeseo-do | Bukgye(北界,북계),Also known as Seobukmyeon(西北面,서북면)) | Pyeongan | — |
Provinces of Joseon
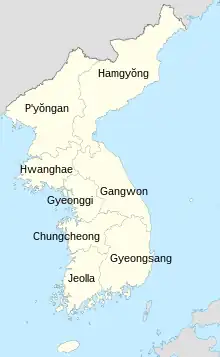
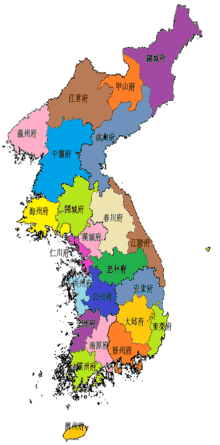
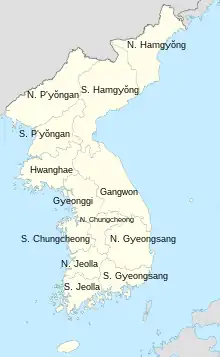
In 1413, Korea (at that time called Joseon) was divided into eight provinces: Chungcheong, Gangwon, Gyeonggi, Gyeongsang, Jeolla, Hamgyŏng (originally called Yeonggil), Hwanghae (originally called P'unghae), and P'yŏngan.
Districts of Late Joseon period
In 1895, Korea was redivided into 23 districts (Bu; 부; 府), each named for the city or county that was its capital. The districts were short-lived, however, as the following year, the provincial system was restored.
Provinces of the Korean Empire
In 1896, the former eight provinces were restored, with five of them (Chungcheong, Gyeongsang, Jeolla, Hamgyŏng, and P'yŏngan) being divided into North and South Provinces (Bukdo (북도; 北道) and Namdo (남도; 南道) respectively). The resulting system of thirteen provinces lasted until the Division of Korea in 1945.
The thirteen provinces were: North and South Chungcheong, Gangwon, Gyeonggi, North and South Gyeongsang, North and South Hamgyŏng, Hwanghae, North and South Jeolla, and North and South P'yŏngan.
Provinces of Chōsen
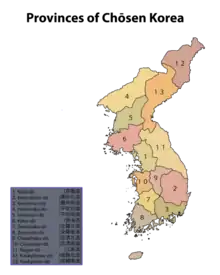
Under Colonial Japanese rule, Korean provinces of Korean Empire, remained much the same, only taking on the Japanese reading of the hanja. The Provinces of Chōsen were:
| Japanese name | Kanji | Kana | Korean name | Hangul |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chūseihoku-dō | 忠清北道 | ちゅうせいほくどう | Chungcheongbuk-do | 충청북도 |
| Chūseinan-dō | 忠淸南道 | ちゅうせいなんどう | Chungcheongnam-do | 충청남도 |
| Keishōhoku-dō | 慶尚北道 | けいしょうほくどう | Gyeongsangbuk-do | 경상북도 |
| Keishōnan-dō | 慶尚南道 | けいしょうなんどう | Gyeongsangnam-do | 경상남도 |
| Heianhoku-dō | 平安北道 | へいあんほくどう | Pyeonganbuk-do | 평안북도 |
| Heian'nan-dō | 平安南道 | へいあんなんどう | Pyeongannam-do | 평안남도 |
| Kōgen-dō | 江原道 | こうげんどう | Gangwon-do | 강원도 |
| Kōkai-dō | 黃海道 | こうかいどう | Hwanghae-do | 황해도 |
| Kankyōhoku-dō | 咸鏡北道 | かんきょうほくどう | Hamgyeongbuk-do | 함경북도 |
| Kankyōnan-dō | 咸鏡南道 | かんきょうなんどう | Hamgyeongnam-do | 함경남도 |
| Zenranan-dō | 全羅南道 | ぜんらなんどう | Jeollanam-do | 전라남도 |
| Zenrahoku-dō | 全羅北道 | ぜんらほくどう | Jeollabuk-do | 전라북도 |
| Keiki-dō | 京畿道 | けいきどう | Gyeonggi-do | 경기도 |
Provincial divisions since the division of Korea
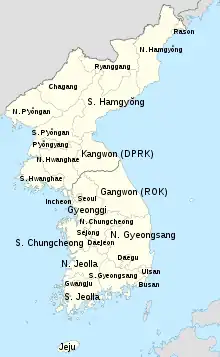
At the end of World War II in 1945, Korea was divided into Northern Korea and Southern Korea under trusteeship of the Soviet Union and the United States. The peninsula was divided at the 38th parallel in 1945. In 1948, the two zones became the independent countries of North Korea and South Korea.
Three provinces—Hwanghae, Gyeonggi, and Gangwon—were divided by the 38th parallel.
- Most of Hwanghae Province belonged to the Northern zone. The southern portion became part of Gyeonggi Province in the south.
- Most of Gyeonggi Province belonged to the Southern zone. In 1946, the northern portion became part of Hwanghae Province in the north.
- Gangwon Province was divided roughly in half, to form modern-day Gangwon Province in South Korea and Kangwon Province in North Korea. The northern province is expanded in 1946 to include some area around the city of Wonsan (Originally part of South Hamgyong Province)
Also in 1946, the cities of Seoul in the south and Pyongyang in the north separated from Gyeonggi and South Pyongan Provinces respectively to become Special Cities. Both North Korea and South Korea have subsequently upgraded other cities to a level equal to a province, and these cities (special cities of North Korea and special cities of South Korea [qq.v.]) are sometimes counted along with provinces.
Finally, the new provinces of Jeju Province (in the south, in 1946) and Chagang Province (in the north, 1949) were formed, from parts of South Jeolla and North Pyongan respectively. In 1954, Ryanggang Province was split from South Hamgyong and Hwanghae was divided into North and South Hwanghae Provinces.
The following table lists the present provincial divisions in the Korean Peninsula.
- Notes
- 1 See Names of Seoul.
See also
- List of South Korean regions by GDP
- List of provinces of Balhae
Notes
- Initially installed from part of Donggye in 1178 as Chunchudo(춘주도,春州道).Was once called Dongjudo(동주도,東州道) but named as gyojudo in 1263.From 1314 to 1388 it was known as Hoeyangdo(회양도,淮陽道)as a result of demotion of Gyojumok under Hoeyang.From 1388 to 1392, it was known as gyojugangneungdo after merging with gangneungdo(강릉도,江陵道).
- "Gwandong" is the name for the region as a whole, with "Yeongseo" denoting the western half of the province and "Yeongdong" the eastern half. "Yeongdong" is used more often than either of the other two terms, however, especially in reference to railway and road arteries that cross through Gangwon, connecting the Seoul and Yeongdong regions.
- The province's name literally means "area within a 500-li (200-km) radius" (gi; 畿) of the "capital" (Gyeong; 京), referring to the royal capital Hanseong (modern-day Seoul). The regional name "Gijeon" is obsolete. The 20th-century term "Sudogwon" ("Capital Region") is used today to denote the Seoul-Incheon conurbation and that part of Gyeonggi Province that forms part of the same built-up, urban area.
- "Gwanbuk" was used to designate either the province as whole, or only the northern part thereof. In the latter case, "Gwannam" was then used to denote the southern part of the province.
- The modern-day division of the province into North and South did not occur until 1954.
- The initial "n" in "Naju" is pronounced as "l" (lower-case "L") when it comes after another consonant; the final "n" in the "Jeon" of "Jeonju" is then assimilated to an "l" sound.
- The distinctive Jeju dialect is used on Jeju Island, which became a separate province in 1946.
References
- "Unified Silla Dynasty". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2024-04-26.
- 이, 기동, "신라 (新羅)", Encyclopedia of Korean Culture (in Korean), Academy of Korean Studies, retrieved 2024-04-26
- 전, 덕재, "오소경 (五小京)", Encyclopedia of Korean Culture (in Korean), Academy of Korean Studies, retrieved 2024-04-26
- 박, 성현, "구주 (九州)", Encyclopedia of Korean Culture (in Korean), Academy of Korean Studies, retrieved 2024-04-26
- 박, 종기(국민대 명예교수), "고려 (高麗)", Encyclopedia of Korean Culture (in Korean), Academy of Korean Studies, retrieved 2024-04-26
- "3경". 우리역사넷. National Institute of Korean History. Retrieved 2024-04-26.
- 김, 현영, "목 (牧)", Encyclopedia of Korean Culture (in Korean), Academy of Korean Studies, retrieved 2024-04-26
- "십도 (十道)", Encyclopedia of Korean Culture (in Korean), Academy of Korean Studies, retrieved 2024-04-26
- "오도 (五道)", Encyclopedia of Korean Culture (in Korean), Academy of Korean Studies, retrieved 2024-04-26
Sources
- Nahm, Andrew C. (1988). Korea: Tradition and Transformation - A History of the Korean People. Elizabeth, NJ: Hollym International.
- Nahm 1988 (in Korean).
External links
- Map of North Korea – World-Gazetteer.com at the Wayback Machine (archived 2002-02-19)
- Map of South Korea – World-Gazetteer.com at the Wayback Machine (archived 2002-05-25)