Queen Alexandra Range
The Queen Alexandra Range (84°00′S 168°00′E) is a major mountain range about 100 nautical miles (190 km; 120 mi) long, bordering the entire western side of Beardmore Glacier from the Polar Plateau to the Ross Ice Shelf.[2] The range is in the Transantarctic Mountains System, and is located in the Ross Dependency region of Antarctica.
| Queen Alexandra Range | |
|---|---|
 Queen Alexandra Range Location in Antarctica | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Mount Kirkpatrick |
| Elevation | 4,528 m (14,856 ft) |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 160 km (99 mi)[1] |
| Area | 74,641 km2 (28,819 sq mi) |
| Geography | |
| Range coordinates | 84°00′S 168°00′E[2] |
Discovery
The Queen Alexandra Range was discovered on the journey toward the South Pole by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09 (BrAE), and was named by Ernest Shackleton for Queen Alexandra, Queen of the United Kingdom, 1901-10.[2] Shackleton and his men, and a later expedition headed by Robert Falcon Scott, both collected rock samples from the range that contained fossils. The discovery that multicellular life forms had lived so close to the South Pole was an additional piece of evidence that accompanied the publication (in 1910 and independently in 1912) of the theory of continental drift.
Location
The Queen Alexandra Range is bounded by the Beardmore Glacier along its southeast edge, which divides it from the Commonwealth Range of the Queen Maud Mountains to the east. The west of the range is bounded by the Antarctic Plateau in the south. Further north it is bounded by the Walcott Névé to the east, which separates the range from the Colbert Hills. The Walcott Névé joins the Law Glacier in the Bowden Névé which feeds the Lennox-King Glacier. This glacier bounds the northwest part of the range, and separates it from the Holland Range to the north. The northern tip of the range extends to the Ross Ice Shelf between the Lennox King Glaciers and Beardmore Glacier.[3][4][5]
Major glaciers
- Beardmore Glacier (83°45′S 171°00′E) is of the largest known valley glaciers, over 100 nautical miles (190 km; 120 mi) long, descending the polar plateau and flowing north between the Queen Alexandra Range and Commonwealth Range, to enter the Ross Ice Shelf.[6]
- Law Glacier (84°05′S 161°00′E) is a glacier about 10 nautical miles (19 km; 12 mi) wide between the south end of the Queen Elizabeth Range and the MacAlpine Hills, gradually descending east-northeast from the polar plateau to Bowden Névé.[7]
- Bowden Névé 83°30′S 165°00′E is a névé about 20 miles (32 km) wide, lying southward of Mount Miller between Queen Elizabeth Range and Queen Alexandra Range.[8]
- Walcott Névé 84°23′S 162°40′E is a névé, about 350 square miles (910 km2) in area, bounded by the Marshall Mountains, Lewis Cliff and Mount Sirius.[9]
- Lennox-King Glacier (83°25′S 168°00′E) is a large valley glacier, about 40 nautical miles (74 km; 46 mi) long, draining Bowden Névé and flowing northeast between the Holland Range and Queen Alexandra Ranges to enter Richards Inlet, Ross Ice Shelf.[10]
Mountains and peaks
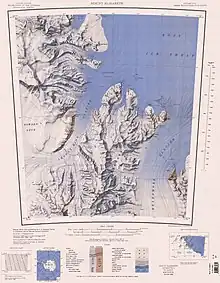


Mountains and peaks over 3,000 metres (9,800 ft) high include:
| Mountain | m | ft | coord |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mount Kirkpatrick | 4,528 | 14,856 | 84°20′S 166°25′E |
| Mount Elizabeth | 4,480 | 14,698 | (83°54′S 168°23′E |
| Mount Bell | 4,305 | 14,124 | 84°04′S 167°30′E |
| Mount Mackellar | 4,295 | 14,091 | 83°59′S 166°39′E |
| Fleming Summit | 4,200 | 13,780 | 84.33333°S 166.3°E |
| Mount Dickerson | 4,120 | 13,517 | 84°20′S 167°08′E |
| Decennial Peak | 4,020 | 13,189 | 84°22′S 166°02′E |
| Mount Anne | 3,870 | 12,697 | 83°48′S 168°30′E |
| Mount Falla | 3,825 | 12,549 | 84°22′S 164°55′E |
| Tempest Peak | 3,410 | 11,188 | 84°31′S 164°11′E |
| Blizzard Peak | 3,375 | 11,073 | 84°38′S 164°08′E |
| Barnes Peak | 3,360 | 11,024 | 84°23′S 167°34′E |
| Storm Peak | 3,280 | 10,761 | 84°35′S 164°00′E |
| Mount Stanley | 3,220 | 10,564 | 84°09′S 165°29′E |
| Lindsay Peak | 3,210 | 10,531 | 84°37′S 163°32′E |
| Mount Marshall | 3,160 | 10,367 | 84°41′S 164°39′E |
| Pagoda Peak | 3,040 | 9,974 | 83°56′S 166°45′E |
| Mount Price | 3,030 | 9,941 | 84°29′S 166°38′E |
| Mount Bishop | 3,020 | 9,908 | 83°43′S 168°42′E |
| Kip Peak | 3,000 | 9,843 | 84.5167°S 164.46667°E |
Features
Major features that are the focus of a named or unnamed group of lesser features, include:
- Morris Heights (83°28′S 169°42′E), a relatively smooth ice-covered heights, forming a peninsula-like divide between Beaver Glacier and King Glacier at the north end of the Queen Alexandra Range.[11]
- Mount Elizabeth (83°54′S 168°23′E), a massive ice-free mountain, 4,480 metres (14,700 ft) high, standing 6 nautical miles (11 km; 6.9 mi) south of Mount Anne.[12]
- Mount Mackellar (83°59′S 166°39′E), a massive mountain, 4,295 metres (14,091 ft) high, standing at the head of Mackellar Glacier, 3 nautical miles (5.6 km; 3.5 mi) south of Pagoda Peak.[13]
- Grindley Plateau (84°9′S 166°5′E), a high icecapped plateau in the central Queen Alexandra Range, bordered by the peaks of Mount Mackellar, Mount Bell and Mount Kirkpatrick.[14]
- The Cloudmaker (84°17′S 169°25′E), a massive mountain, 2,680 metres (8,790 ft) high, standing at the west side of Beardmore Glacier, just south of Hewson Glacier. It is easily identifiable by its high, ice-free slope facing Beardmore Glacier.[15]
- Mount Kirkpatrick (84°20′S 166°25′E), a lofty, generally ice-free mountain in Queen Alexandra Range 5 nautical miles (9.3 km; 5.8 mi) west of Mount Dickerson. At 4,528 metres (14,856 ft) it is the highest point in the Queen Alexandra Range.[16]
- Adams Mountains (84°30′S 166°20′E), a small but well defined group of mountains bounded by the Beardmore Glacier, Berwick Glacier, Moody Glacier and Bingley Glacier.[17]
- Mount Falla (84°22′S 164°55′E), a prominent conical mountain, 3,825 metres (12,549 ft) high, standing 3.5 nautical miles (6.5 km; 4.0 mi) northeast of Mount Stonehouse, between Berwick Glacier and Prebble Glacier.[18]
- Marshall Mountains (84°37′S 164°30′E), a group of mountains overlooking Beardmore Glacier. They are bounded on the north by Berwick Glacier, and on the south by Swinford Glacier.[19]
References
- Queen Alexandra Range PB.
- Alberts 1995, p. 599.
- Buckley Island USGS.
- Mount Elizabeth USGS.
- The Cloudmaker USGS.
- Alberts 1995, p. 53.
- Alberts 1995, p. 423.
- Alberts 1995, p. 84.
- Alberts 1995, p. 791.
- Alberts 1995, p. 428.
- Alberts 1995, p. 506.
- Alberts 1995, p. 217.
- Alberts 1995, p. 453.
- Alberts 1995, p. 297.
- Alberts 1995, p. 141.
- Alberts 1995, p. 394.
- Alberts 1995, p. 4.
- Alberts 1995, p. 232.
- Alberts 1995, p. 464.
Sources
- Alberts, Fred G., ed. (1995), Geographic Names of the Antarctic (PDF) (2 ed.), United States Board on Geographic Names, retrieved 2023-12-03
 This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Board on Geographic Names.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Board on Geographic Names. - Buckley Island, USGS: United States Geological Survey, retrieved 2024-03-16
- Mount Elizabeth, USGS: United States Geological Survey, retrieved 2024-03-16
- "Queen Alexandra Range", Peakbagger, retrieved 25 May 2017
- The Cloudmaker, USGS: United States Geological Survey, retrieved 2024-03-16
 This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Geological Survey.