Lesson 4: Getting Started with Excel
/en/excel2013/understanding-office-365/content/
Introduction
Excel 2013 is a spreadsheet program that allows you to store, organize, and analyze information.
While you may believe Excel is only used by certain people to process
complicated data, anyone can learn how to take advantage of the
program's powerful features. Whether
you're keeping a budget, organizing a training log, or creating an
invoice, Excel makes it easy to work with different types of data.
Getting to know Excel 2013
Excel 2013 is similar to Excel 2010. If you've previously used Excel 2010, Excel 2013 should feel familiar. If you are new to Excel or have more experience with older versions, you should first take some time to become familiar with the Excel 2013 interface.
The Excel interface
When you open Excel 2013 for the first time, the Excel Start Screen will appear. From here, you'll be able to create a new workbook, choose a template, and access your recently edited workbooks.
- From the Excel Start Screen, locate and select Blank workbook to access the Excel interface.
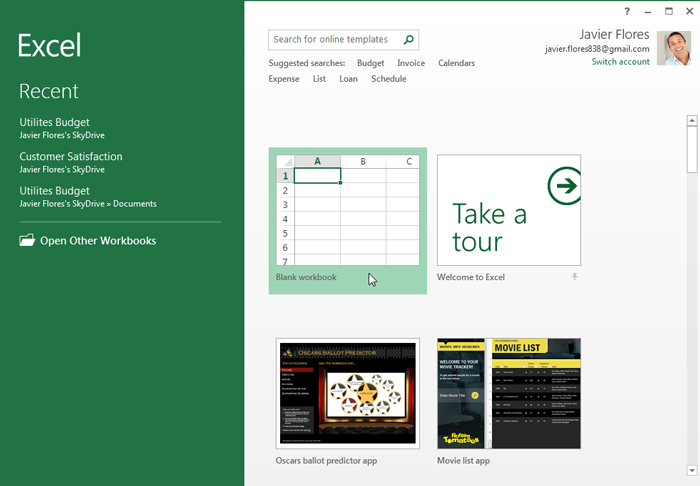 The Excel Start Screen
The Excel Start Screen
Click the buttons in the interactive below to become familiar with the Excel 2013 interface.
Working with the Excel environment
If you've previously used Excel 2010 or 2007, Excel 2013 will feel familiar. It continues to use features like the Ribbon and Quick Access toolbar, where you will find commands to perform common tasks in Excel, as well as Backstage view.
The Ribbon
Excel 2013 uses a tabbed Ribbon system instead of traditional menus. The Ribbon contains multiple tabs, each with several groups of commands. You will use these tabs to perform the most common tasks in Excel.
Click the arrows in the slideshow below to learn more about the different commands available within each tab on the Ribbon.
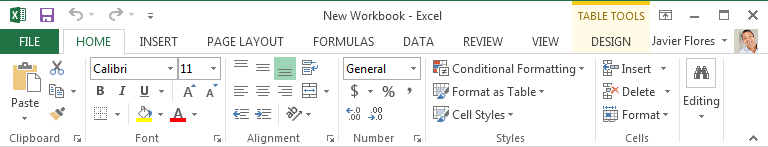
The Home tab gives you access to some of the most commonly used commands for working with data in Excel 2013, including copying and pasting, formatting, and number styles. The Home tab is selected by default whenever you open Excel.
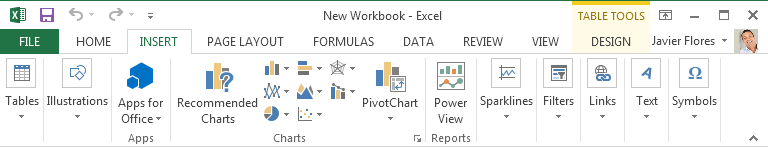
The Insert tab allows you to insert charts, tables, sparklines, filters, and more, which can help you visualize and communicate your workbook data graphically.
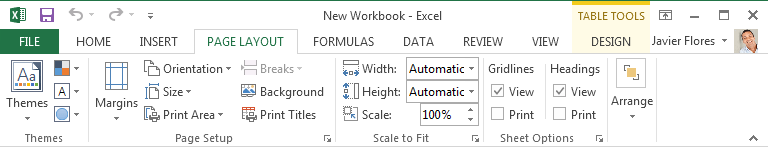
The Page Layout tab allows you to change the print formatting of your workbook, including margin width, page orientation, and themes. These commands will be especially helpful when preparing to print a workbook.
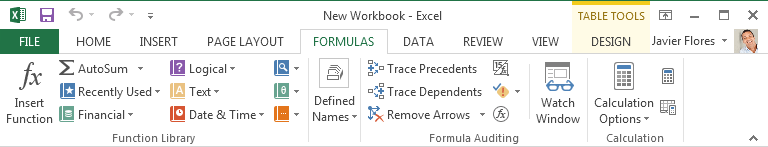
The Formulas tab gives you access to the most commonly used functions and formulas in Excel. These commands will help you calculate and analyze numerical data, such as averages and percentages.
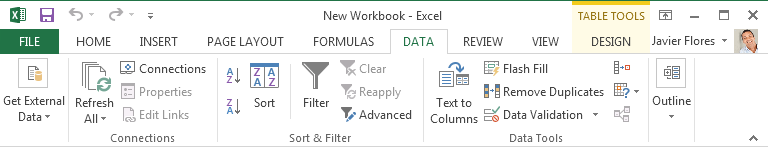
The Data tab makes it easy to sort and filter information in your workbook, which can be especially helpful if your project contains a large amount of data.
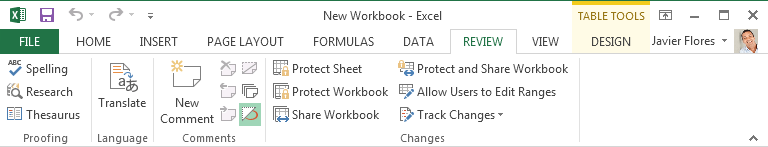
You can use the Review tab to access Excel's powerful editing features, including comments and track changes. These features make it easy to share and collaborate on workbooks.
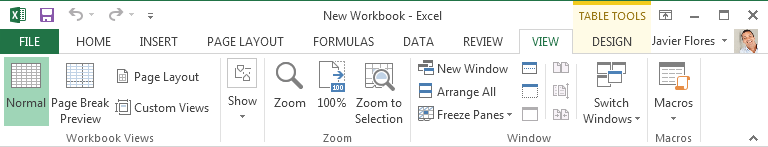
The View tab allows you to switch between different views for your workbook and freeze panes for easy viewing. These commands will also be helpful when preparing to print a workbook.
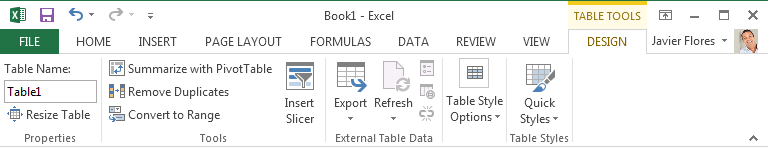
Contextual tabs will appear on the Ribbon when working with certain items, like tables and pictures. These tabs contain special command groups that can help you format these items as needed.
To minimize and maximize the Ribbon:
The Ribbon is designed to respond to your current task, but you can choose to minimize it if you find that it takes up too much screen space.
- Click the Ribbon Display Options arrow in the upper-right corner of the Ribbon.
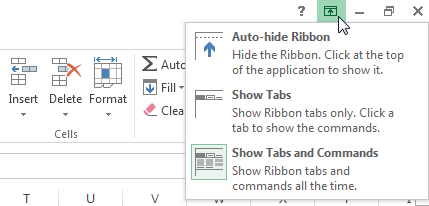 Ribbon Display options
Ribbon Display options - Select the desired minimizing option from the drop-down menu:
- Auto-hide Ribbon: Auto-hide displays your workbook in full-screen mode and completely hides the Ribbon. To show the Ribbon, click the Expand Ribbon command at the top of screen.
 Auto-hiding the Ribbon
Auto-hiding the Ribbon - Show Tabs: This option hides all command groups when they're not in use, but tabs will remain visible. To show the Ribbon, simply click a tab.
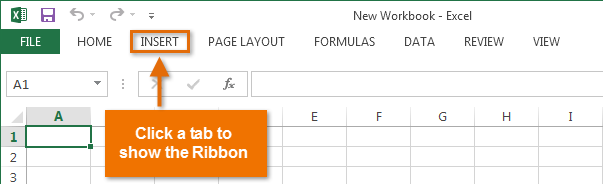 Showing only Ribbon tabs
Showing only Ribbon tabs - Show Tabs and Commands: This option maximizes the Ribbon. All of the tabs and commands will be visible. This option is selected by default when you open Excel for the first time.
To learn how to add custom tabs and commands to the Ribbon, review our Extra on Customizing the Ribbon.
To learn how to use the Ribbon with touch-screen devices, review our Extra on Enabling Touch Mode.
The Quick Access toolbar
Located just above the Ribbon, the Quick Access toolbar lets you access common commands no matter which tab is selected. By default, it includes the Save, Undo, and Repeat commands. You can add other commands depending on your preference.
To add commands to the Quick Access toolbar:
- Click the drop-down arrow to the right of the Quick Access toolbar.
- Select the command you want to add from the drop-down menu. To choose from more commands, select More Commands.
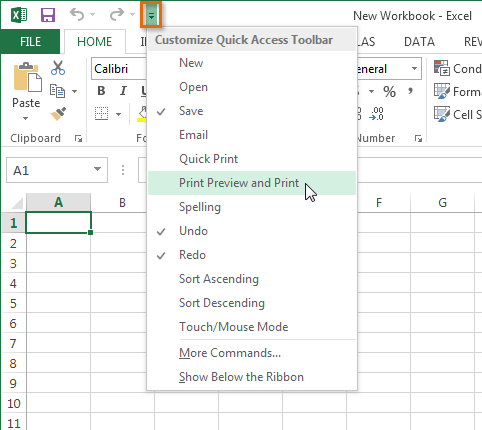 Adding a command to the Quick Access toolbar
Adding a command to the Quick Access toolbar - The command will be added to the Quick Access toolbar.
 The added command
The added command
Backstage view
Backstage view gives you various options for saving, opening a file, printing, and sharing your workbooks.
To access Backstage view:
- Click the File tab on the Ribbon. Backstage view will appear.
 Clicking the File tab
Clicking the File tab
Click the buttons in the interactive below to learn more about using Backstage view.
Worksheet views
Excel 2013 has a variety of viewing options that change how your workbook is displayed. You can choose to view any workbook in Normal view, Page Layout view, or Page Break view. These views can be useful for various tasks, especially if you're planning to print the spreadsheet.
- To change worksheet views, locate and select the desired worksheet view command in the bottom-right corner of the Excel window.
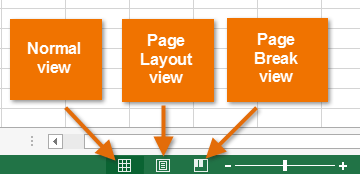 Worksheet view options
Worksheet view optionsClick the arrows in the slideshow below to review the different worksheet view options.
Normal view: This is the default view for all worksheets in Excel.
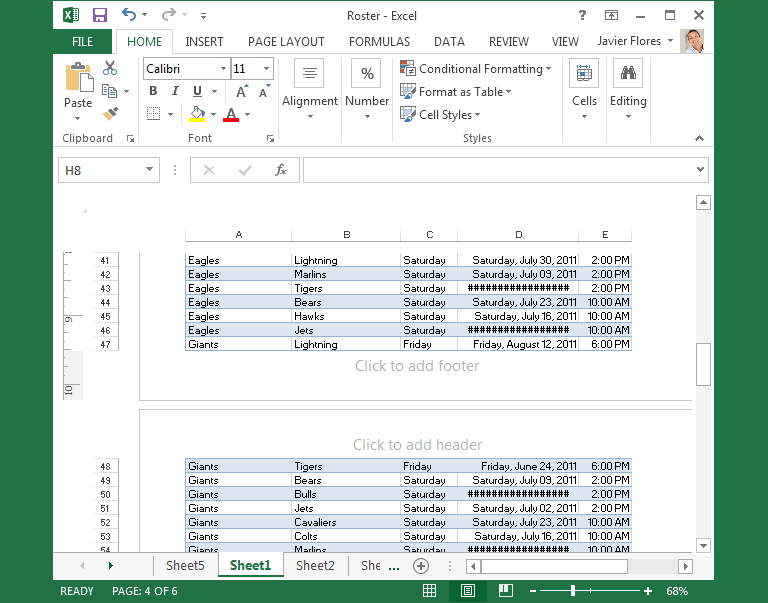
Page Layout view: This view can help you visualize how your worksheet will appear when printed. You can also add headers and footers from this view.
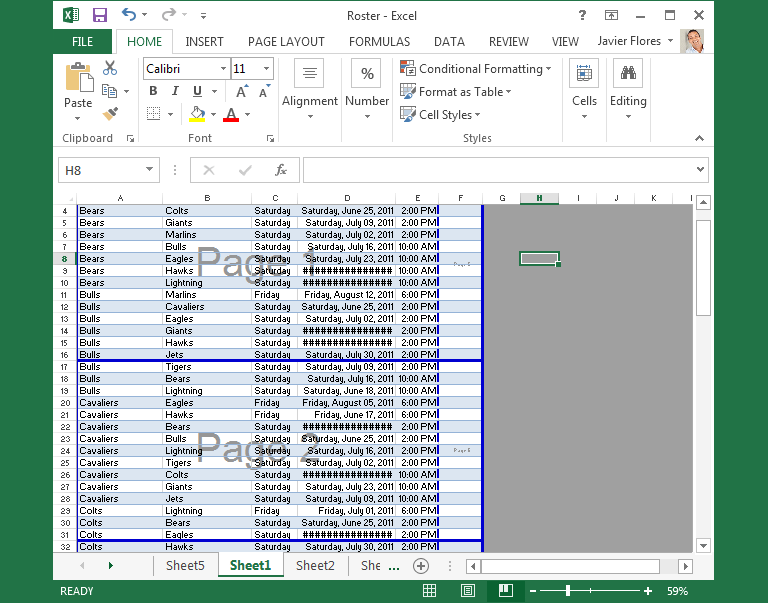
Page Break view: This view makes it easy to change the location of page breaks in your workbook, which is especially helpful when printing a lot of data from Excel.
Challenge!
- Open Excel 2013.
- Click through all of the tabs, and review the commands on the Ribbon.
- Try minimizing and maximizing the Ribbon.
- Add a command to the Quick Access toolbar.
- Navigate to Backstage view, and open your Account settings.
- Try switching worksheet views.
- Close Excel (you do not have to save the workbook).
/en/excel2013/creating-and-opening-workbooks/content/


 The Excel Start Screen
The Excel Start Screen
 Ribbon Display options
Ribbon Display options Auto-hiding the Ribbon
Auto-hiding the Ribbon Showing only Ribbon tabs
Showing only Ribbon tabs Adding a command to the Quick Access toolbar
Adding a command to the Quick Access toolbar The added command
The added command Clicking the File tab
Clicking the File tab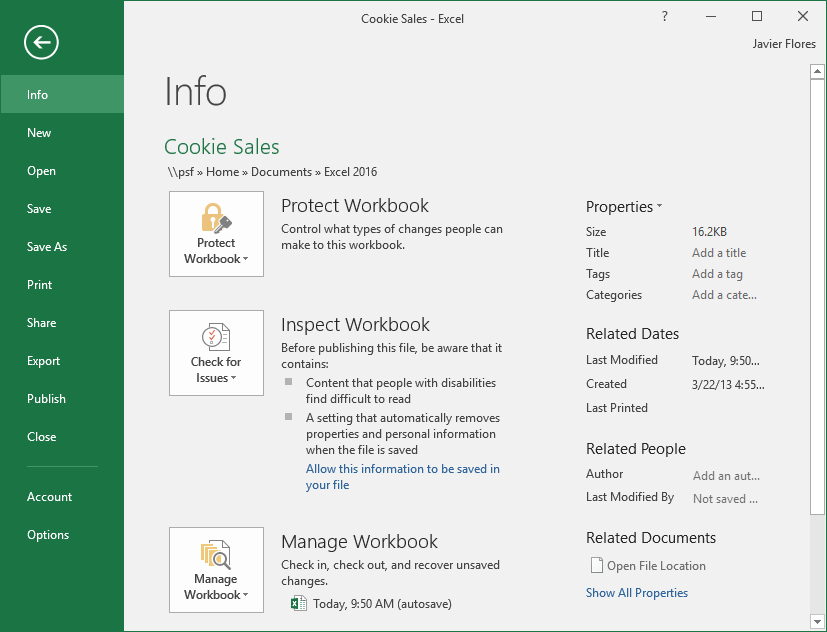
 Worksheet view options
Worksheet view options