This article was co-authored by Luigi Oppido and by wikiHow staff writer, Nicole Levine, MFA. Luigi Oppido is the Owner and Operator of Pleasure Point Computers in Santa Cruz, California. Luigi has over 25 years of experience in general computer repair, data recovery, virus removal, and upgrades. He is also the host of the Computer Man Show! broadcasted on KSQD covering central California for over two years.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article's instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 3,406,785 times.
This wikiHow teaches you how to improve signal strength and minimize interference on your home wireless network. Your ability to maintain a consistent connection to Wi-Fi depends on many factors, including the physical location of your wireless access point. Placing your router in the best possible location and minimizing interference (both physical and wireless) can greatly improve network performance.
Steps
-
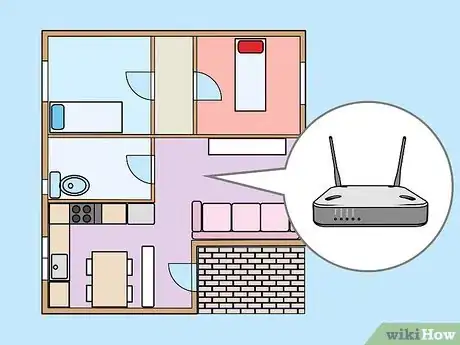
1Remove physical obstructions between your computer and the router. A Wi-Fi signal can usually travel about 1000 feet, but every wall drops that by about 100 feet. To maintain the most reliable connection, make sure your computer has line-of-sight access to the router. If that's not possible, you can still improve reception by minimizing some barriers:
- Place the router high up, such as on a wall mount or high shelf.[1] If the router is on the floor or on a low table, you'll be wasting much of the router's signal 360-degree range.[2]
- Glass from mirrors and windows reflect Wi-Fi signals back around the room. If you can't move the router away from glass, try covering the glass with a curtain or cloth.
- Thicker walls, such as those made of brick, concrete, or stone, seriously impact signal strength. You may also run into trouble if your walls contain metal ducts, studs, and pipes. If your walls are impeding the Wi-Fi signal, open the door to the room where your router is, and place the router is as close to it as possible.
- Tall furniture and appliances can block signals, especially when leaning against thick walls. Avoid setting up your wireless router in rooms with lots of tall objects.
-
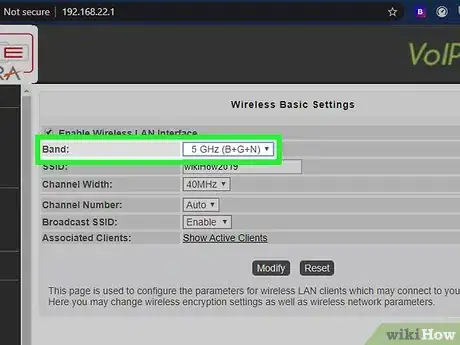
2Switch to 5 GHz.[3] If you have a dual-band router (2 GHz and 5 GHz), log in to your router's admin website and switch the wireless band setting to 5 GHz.[4] Because fewer devices operate at this frequency, this band is less crowded, resulting in a speedier and more reliable wireless connection.[5]Advertisement
-
3Eliminate 2.4 GHz wireless interference. If you're using 5 GHz you can skip this step. If your only option is 2.4 GHz, interference from common household electronics and neighboring networks can lead to dropped connections and slow speeds. Try minimizing interference from the following sources:
- Your neighbor's wireless network. Move your router closer to the center of your home or office if your neighbor's router is too close to yours.
- 2.4 GHz cordless phones and Bluetooth accessors.
- High-voltage household items like air conditioners, microwaves, refrigerators, and washing machines.
- Baby monitors and wireless security equipment.
-
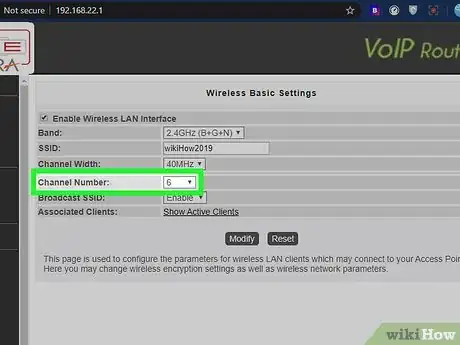
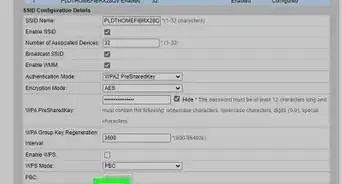
4Connect the Wi-Fi router to a less-busy channel. If too many of your neighbors are using the same Wi-Fi channel, your connection is likely slow and/or spotty.[6] Try a free Wi-Fi scanning tool like inSSIDer by MetaGeek to identify the least crowded channel to connect to.
- If you have a 2.4 GHz wireless router, you'll want to make sure it is connected to one of the three non-overlapping channels—1, 6, or 11. This can be done in your router's administration portal in the Wi-Fi or Wireless section. Look for a sub-menu called Radio or Channel.
- If you have a 5 GHz router, there's less chance of a crowded channel resulting in a slow connection, though it's still possible.
-
5Add a wireless range extender or additional antennas. If it's not possible to be within 50 to 100 feet of your router and/or there are physical obstructions, you can use a range extender to rebroadcast your router's Wi-Fi signal in other parts of your home or office.[7] You can also try adding more antennas.[8] For example, you might have one antenna at a 45° angle, one at 60°, and one at 35°. That way, the signal will blanket the area.
- See this wikiHow to learn how to set up a range extender.
- Another option is a mesh router.[9] This type of router consists of multiple access points placed throughout the home to boost signal in those locations. The advantage of a mesh router to a range extender is that you can manage all of the access points from one central admin interface.
-
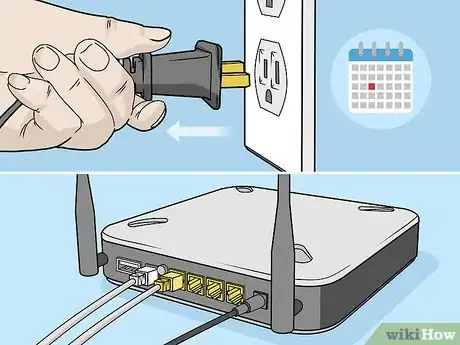
6Restart your router at least once a month. To do this, turn off the router, wait for 30 seconds, and then turn it back on. Let it run for about 5 minutes, and then check your internet speed.
-
7Create an aluminum foil reflector. If you're unable to boost your Wi-Fi signal far enough and don't have a repeater or mesh router, you can make a parabolic reflector out of aluminum foil to place behind your router's antennas. Here's how:
- Cut about 11" of aluminum foil from the roll.
- Tightly wrap the foil around a 2-liter soda bottle.
- Unwrap the foil after a few seconds—it should now be curved.
- Place the curved foil behind the antennas of the router so the open part of the curve is facing the direction you want to send a higher level of signal.
-
8Disconnect unused computers and accessories from the network. If you have multiple computers, phones, tablets, printers, Smart TVs, and other accessories using your wireless network at once, you might be slowing down your wireless network. Turn off or disconnect the devices you aren't using to improve network speeds for those you are using.
- You can limit the number of devices your router will allow to connect at a time. This is typically done by logging in to your router's administrator website and adjusting settings in the LAN or Local Network area.
-
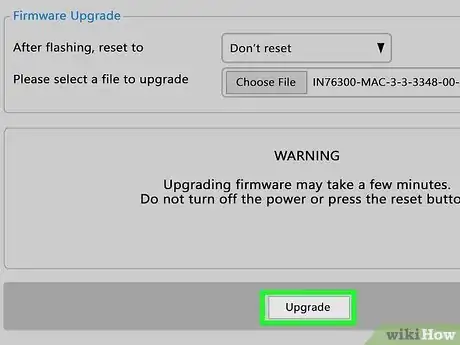
9Update your router's firmware. If you're still experiencing poor reception, your router may be in need of a firmware update. This can usually be done in your router's admin portal, but some routers require additional steps. See this wikiHow to learn the basics of updating your router's firmware.
-
10Get a new router about every 3 years.[10] If you've had your router for 3 or more years, it's probably time to replace it. That's about their average lifespan, since they're typically on 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, and they're often exposed to things like power outages or surges.
Community Q&A
Did you know you can get answers researched by wikiHow Staff?
Unlock staff-researched answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionWhich wireless channel to use?
 wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Staff Answer wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerWhen choosing a wireless channel to use for optimal WiFi signals, try to find one that people around you are not using. Many routers choose a default for you but if that appears to be getting interference in your home, then try channels 1, 6 or 11 instead because these are known as non-overlapping channels. On other channels, co-channel interference can occur where other WiFi devices are trying to use the same channel, which can slow down the transfer while each device “takes its turn.” You will still need to work out if the neighbors are also using 1, 6 or 11 and there are tools that allow you to do this, so download one, use it, then choose the channel with the least or no other users on it.
wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerWhen choosing a wireless channel to use for optimal WiFi signals, try to find one that people around you are not using. Many routers choose a default for you but if that appears to be getting interference in your home, then try channels 1, 6 or 11 instead because these are known as non-overlapping channels. On other channels, co-channel interference can occur where other WiFi devices are trying to use the same channel, which can slow down the transfer while each device “takes its turn.” You will still need to work out if the neighbors are also using 1, 6 or 11 and there are tools that allow you to do this, so download one, use it, then choose the channel with the least or no other users on it. -
QuestionHow can I boost my WiFi signal?
 wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Staff Answer wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerWays to boost your WiFi signal include: Using a WiFi booster, either a commercial or homemade one; shifting your router’s position to find an optimal placement in your home or office; shifting large furniture to external walls, to prevent signal blocking; reducing the amount of mirrors in your home; if you have a two-story house, place the router on the top floor to allow the radio waves to travel downward; and locate the router centrally. Replace your router after several years too, as the older it gets, the less effective it is likely to be. Details for these suggestions and more are fully explained in the steps above.
wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerWays to boost your WiFi signal include: Using a WiFi booster, either a commercial or homemade one; shifting your router’s position to find an optimal placement in your home or office; shifting large furniture to external walls, to prevent signal blocking; reducing the amount of mirrors in your home; if you have a two-story house, place the router on the top floor to allow the radio waves to travel downward; and locate the router centrally. Replace your router after several years too, as the older it gets, the less effective it is likely to be. Details for these suggestions and more are fully explained in the steps above. -
QuestionDo WiFi boosters really work?
 wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff EditorThis answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Staff Answer wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerYes, the WiFi booster will work, provided you buy a quality booster that has had good reviews. It will work to increase the range of WiFi throughout a residential building or other building. Be sure to follow the instructions that come with the booster and use it within the spatial area it is recommended for. No booster can solve a WiFi problem in an area larger than what it’s designed for.
wikiHow Staff EditorStaff AnswerYes, the WiFi booster will work, provided you buy a quality booster that has had good reviews. It will work to increase the range of WiFi throughout a residential building or other building. Be sure to follow the instructions that come with the booster and use it within the spatial area it is recommended for. No booster can solve a WiFi problem in an area larger than what it’s designed for.
Warnings
- If you turn the power up too high on a modified wireless router it may suffer permanent damage.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- If you replace your router's firmware, it may void your warranty. If not done properly it can damage your router irreparably.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ Luigi Oppido. Computer & Tech Specialist. Expert Interview. 20 August 2019.
- ↑ https://support.shaw.ca/t5/internet-articles/about-wifi-interference/ta-p/6692
- ↑ Luigi Oppido. Computer & Tech Specialist. Expert Interview. 20 August 2019.
- ↑ https://www.laptopmag.com/articles/how-to-use-the-5-ghz-band-on-your-router
- ↑ https://www.laptopmag.com/articles/how-to-use-the-5-ghz-band-on-your-router
- ↑ https://www.metageek.com/training/resources/why-channels-1-6-11.html
- ↑ https://www.pcmag.com/how-to/10-ways-to-boost-your-wi-fi-signal
- ↑ Luigi Oppido. Computer & Tech Specialist. Expert Interview. 20 August 2019.
- ↑ https://www.tomsguide.com/us/best-wifi-routers,review-2498.html
- ↑ Luigi Oppido. Computer & Tech Specialist. Expert Interview. 20 August 2019.
About This Article
1. Remove physical obstructions.
2. Switch to 5 GHz.
3. Eliminate network interference.
4. Log into the router and change the channel.
5. Keep router far from cordless phones and microwaves.
6. Use a repeater or try a mesh router.
7. Place a curved sheet of foil behind the router.
8. Update the router firmware.






-Connection-Step-12-Version-5.webp)












-Connection-Step-12-Version-5.webp)