High-speed rail in Switzerland
High-speed rail in Switzerland consists of two new lines and three new base tunnels, including the world's longest railway and deepest traffic tunnel:[1] the Gotthard Base Tunnel whose length is 57 km (35 mi). Each of these tunnels have a technical maximum speed of 250 km/h (155 mph), which is reduced, at least in the Gotthard Base Tunnel and the Ceneri Base Tunnel to a maximal authorized speed of 230 km/h (143 mph) for ecological and economical reasons, while the normal operational speed of passenger trains is restricted to 200 km/h (124 mph) in order to accommodate the freight traffic, with the possibility to accelerate up to 230 km/h (143 mph) in case of delay.[2]

History
To address transalpine freight and passenger bottlenecks on its roads and railways, Switzerland launched the Rail 2000 and NRLA projects.

Rail 2000
The first stage of the Rail 2000 project finished in 2005, included a new high-speed rail track between Bern and Olten with an operating speed of 200 km/h (124 mph).
The second stage of Rail 2000, still in project, includes line upgrades in the Valais canton (200 km/h (124 mph)) and between Biel and Solothurn (also 200 km/h (124 mph)).
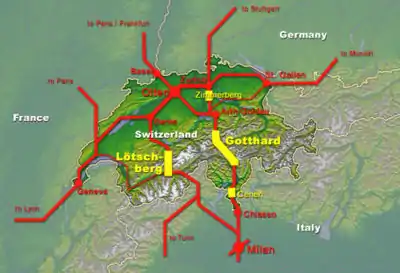
NRLA project
New Railway Link through the Alps (NRLA; German: Neue Eisenbahn-Alpentransversale, NEAT, French: nouvelle ligne ferroviaire à travers les Alpes, NLFA, Italian: Nuova ferrovia transalpina, NFTA), is a Swiss construction project for faster north-south rail links across the Swiss Alps. It includes three completed base tunnels several hundred metres below the existing apex tunnels, the 57-kilometre (35 mi) Gotthard Base Tunnel, the 35-kilometre (22 mi) Lötschberg Base Tunnel, and the 15-kilometre (9.3 mi) Ceneri Base Tunnel.[3] The NRLA also includes the Zimmerberg Base Tunnel for which only Phase I has been completed, in 2003, with an operating speed of 160 km/h (99 mph), and Phase II remains in project.
NRLA project is building faster north-south tracks across the Swiss Alps by constructing base tunnels several hundred metres below the level of the current tunnels. The 35 km (22 mi) Lötschberg Base Tunnel opened in 2007 where New Pendolino trains run. The 57 km (35 mi) Gotthard Base Tunnel opened on 1 June 2016. The 15 km (9.3 mi) Ceneri Base Tunnel opened on 4 September 2020.
However, the slow speed of lines between the NRLA tunnels (Ceneri Base Tunnel, Gotthard Base Tunnel and Zimmerberg Base Tunnel to name but a few) means that the capacity of Zürich-Milan services will remain limited until the speeds can be increased, given the strong negative effect of mixed rail speeds on capacity.
Rolling stock
.jpg.webp)
The fastest Swiss train is the SBB RABe 501 also named Giruno. It is operated by the Swiss Federal Railways since May 2016. They can reach higher speeds than conventional trains on the curve-intensive Swiss network, however the top speed of 200 km/h (124 mph) can only be reached on high-speed lines.
The French-Swiss co-operation TGV Lyria and German ICE lines extend into Switzerland, the ICE 4 regularly operates at a maximum of 200 km/h (124 mph) (between Olten and Bern), while the TGV never exceeds 160 km/h (99 mph), due to the lack of a high-speed track between Basel and Zurich.
The former Cisalpino consortium owned by the Swiss Federal Railways and Trenitalia used Pendolino tilting trains on two of its international lines. These trains are now operated by the Swiss Federal Railways and Trenitalia.
Network
| Line | Max speed | Operating speed (passenger) | Length | Construction began | Construction completed or start of revenue services |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mattstetten–Rothrist new line | 200 km/h | 200 km/h | 45 km | 1996 | 2004 |
| Solothurn-Wanzwil new line | 200/140 km/h (per section) | 200/140 km/h (per section) | 12 km | 2004 | |
| Lötschberg Base Tunnel | 250 km/h | 200 km/h | 35 km | 1994 | 2007 |
| Gotthard Base Tunnel | 250/230 km/h (technical/authorized) | 200/230 km/h (normal/if delay) | 57 km | 1999 | 2016 |
| Ceneri Base Tunnel | 250/230 km/h (technical/authorized) | 200/230 km/h (normal/if delay) | 15 km | 2006 | 2020 |
See also
References
- "Gotthard- und CeneriBasistunnel: die neue Gotthard-Bahn nimmt Gestalt an" (PDF). Geomatik Schweiz. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- Axe nord-sud du Saint-Gothard (Swiss Federal Railways website).
- "Overview". AlpTransit Portal. Berne, Switzerland: Federal Swiss Archives FSA, Federal Office of Transport FOT. Retrieved 2017-07-01.