Portal:Aviation
| Main page | Categories & Main topics | Tasks and Projects |
The Aviation Portal
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. Aircraft includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air balloons and airships.
Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896; then a large step in significance came with the construction of the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet which permitted a major form of transport throughout the world. (Full article...)
Selected article
.jpg.webp)
Selected image
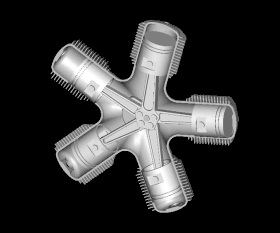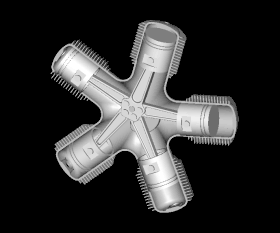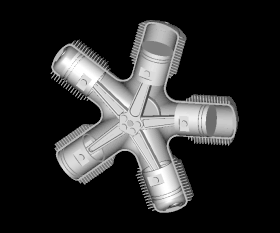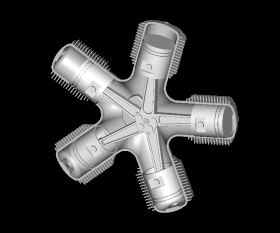
Did you know

...that the Fokker Spin (pictured) was the first aircraft built by Anthony Fokker, in which he taught himself to fly and earned his pilot license? ...that on May 3, 2002 a military MiG-21bis aircraft crashed into the Bank of Rajasthan in India, killing eight? ... that the PZL SM-4 Łątka never flew, because its engine was not approved for use in flight?
General images -
In the news
- May 29: Austrian Airlines cancels Moscow-bound flight after Russia refuses a reroute outside Belarusian airspace
- August 8: Passenger flight crashes upon landing at Calicut airport in India
- June 4: Power firm helicopter strikes cables, crashes near Fairfield, California
- January 29: Former basketball player Kobe Bryant dies in helicopter crash, aged 41
- January 13: Iran admits downing Ukrainian jet, cites 'human error'
- January 10: Fire erupts in parking structure at Sola Airport, Norway
- October 27: US announces restrictions on flying to Cuba
- October 3: World War II era plane crashes in Connecticut, US, killing at least seven
- September 10: Nevada prop plane crash near Las Vegas leaves two dead, three injured
- August 6: French inventor Franky Zapata successfully crosses English Channel on jet-powered hoverboard
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Selected biography
.jpg.webp)
Mitchell deployed to France in 1917 when the United States entered World War I. While there he was promoted to brigadier general and placed in command American combat air units in France. After the war Mitchell was appointed the deputy director of the Air Service became a passionate advocate of air power. In 1921 he set up a demonstration to show the capability of airpower against naval vessels. During the course of the demonstrations aircraft successfully sank a captured German destroyer, the light crusier Frankfurt, and the battleship Ostfriesland.
Mitchell regularly sparred with his superiors over the role of airpower in the military. In 1925 he was reverted to his permanent rank of colonel and was transferred to San Antonio, Texas. Later that year, after a series of aviation accidents he accused Army and Navy leadership of incompetence and "almost treasonable administration of the national defense." In response he was court-martialed for insubordination, found guilty, and sentenced to a five-year suspension from active duty. Mitchell resigned on 1 February 1926 in lieu of serving the sentence. He continued to advocate airpower as a civilian until his death in 1936. In 1942 President Franklin Roosevelt posthumously promoted Mitchell to major general in recognition of his contributions to air power.
Selected Aircraft

The Avro Lancaster was a British four-engine Second World War bomber aircraft made initially by Avro for the British Royal Air Force (RAF). It first saw active service in 1942, and together with the Handley-Page Halifax it was one of the main heavy bombers of the RAF, the RCAF and squadrons from other Commonwealth and European countries serving within RAF Bomber Command. The "Lanc" or "Lankie," as it became affectionately known, became the most famous and most successful of the Second World War night bombers, "delivering 608,612 tons of bombs in 156,000 sorties." Although the Lancaster was primarily a night bomber, it excelled in many other roles including daylight precision bombing, and gained worldwide renown as the "Dam Buster" used in the 1943 Operation Chastise raids on Germany's Ruhr Valley dams.
- Span: 102 ft (31.09 m)
- Length: 69 ft 5 in (21.18 m)
- Height: 19 ft 7 in (5.97 m)
- Engines: 4× Rolls-Royce Merlin XX V12 engines, 1,280 hp (954 kW) each
- Maximum Speed: 240 knots (280 mph, 450 km/h) at 15,000 ft (5,600 m)
- First Flight: 8 January 1941
- Number built: 7,377
Today in Aviation
- 2011 – (Overnight) NATO aircraft raid Libyan Navy bases at Tripoli, Khoms, and Sirte in the largest attack against Libyan government naval forces thus far in the Libyan Civil War. During the Khoms raids, British aircraft hit two corvettes at Khoms with laser-guided bombs and damage an inflatable-boat manufacturing facility, and NATO aircraft set a warship at Tripoli afire. NATO aircraft also hit a police academy in Tripoli's Tajoura neighborhood.[1]
- 2009 – A Lockheed C-130 Hercules of the Indonesian Air Force crashes at Magetan killing 97 people on board the aircraft and a further two on the ground. (This is repeated on 20 May.)
- 2009 – A United States Navy Sikorsky HH-60H Seahawk crashes into the Pacific Ocean 16 miles (26 km) SW of San Diego, California. The aircraft was on a routine training flight and returning to the aircraft carrier USS Nimitz when the accident occurred off of Point Loma, California, killing all 5 members of its crew. Only 3 bodies were recovered.
- 2008 – First flight of the Sukhoi Superjet 100, Russian modern fly-by-wire regional jet in the 75- to 95-seat category.
- 2003 – CH-46E Sea Knight 156424 of HMM-364 crashes in Al-Hilla, killing four Marines; another Marine drowns trying to rescue the crew.[2]
- 2000 – Death of Yevgeni Vassilyevich Khrunov, Soviet cosmonaut.
- 1996 – Launch: Space Shuttle Endeavour STS-77 at 6:30:00.066 am EDT. Mission highlights: SPACEHAB; SPARTAN, Canadian astronaut Marc Garneau's second trip into space.
- 1993 – SAM Colombia Flight 501, a Boeing 727, crashes into Mount Paramo Frontino, killing all 132 on board.
- 1993 – Sikorsky VH-60A Sea Hawk, BuNo 163267,1] of HMX-1, MCAS Quantico, Virginia, crashes ~35 miles SW of Washington, D.C. during a routine inspection flight, killing Maj. William S. Barkley Jr., Capt. Scott J. Reynolds, Staff Sgt. Brian D. Haney, and Sgt. Timothy D. Sabel.
- 1982 – A Royal Navy Westland Sea King HC.4 ZA294, transferring from HMS Hermes to HMS Intrepid during the Falklands/Malvinas conflict, crashes into the sea after a bird strike with a Black-browed Albatross. The crash results in 22 fatalities including 18 members of the 22 Squadron SAS, one fatality each from the Royal Signals and Royal Air Force.
- 1978 – McDonnell Douglas delivers its 5,000th F-4 Phantom II aircraft, twenty years after the first flight of the prototype.
- 1978 – First prototype Sikorsky YUH-60A Black Hawk, 73-21650, crashes during testing at the Sikorsky plant, Stratford, Connecticut, killing three company personnel. Army investigation reveals that during routine maintenance the night before the fatal flight, the airspeed sensor for the tailplane actuating system was inadvertently left unconnected. As the aircraft transitioned from hover to forward flight, the tailplane did not automatically change its angle and as speed built up, it forced the helicopter's nose down until an attitude was reached from which recovery was impossible. A manual back-up system was available and functioning, and could have been used to correct the tailplane angle, but for unexplained reasons it was not used, possibly due to failure to analyze the nature of the problem in time. Minor modifications are introduced as a result of this accident.
- 1977 – First flight of the Sukhoi T-10 (prototype of Sukhoi Su-27).
- 1971 – Boeing announces that it has canceled its Supersonic Transport (SST) project.
- 1971 – Launch of Mars 2, Soviet unmanned lander and orbiter, first human artifacts to impact the surface of Mars.
- 1967- First flight of Dassault Mirage 5, French supersonic attack aircraft.
- 1965 – Pakistan International Airlines Flight 705, a Boeing 720-040 B on an inaugural flight carrying mostly journalists and owners of travel agencies and crewed by what the airline considered its best crew members, crashes short of the runway while descending to land at Cairo International Airport in Cairo, Egypt, killing 119 of the 125 people on board and injuring all six survivors.
- 1961 – Venera 1, first planetary probe launched to Venus by the Soviet Union, passed within 100,000 km of Venus and entered a heliocentric orbit.
- 1958 – Vickers Viscount N7410 of Capital Airlines collides in mid-air with a Lockheed T-33 Shooting Star of the Air National Guard. All eleven on board the Viscount are killed when it crashes at Brunswick, Maryland, as is one of the two crew members of the T-33. (This is repeated on 20 May)
- 1956 – First flight of the Aerfer Sagittario 2, Italian prototype all-metal single-seat lightweight fighter aircraft, first Italian aircraft to break the sound barrier in controlled flight.
- 1955 – Birth of Pierre Joseph Thuot, retired U. S. Navy captain and NASA astronaut
- 1952 – First flight of the Grumman XF10F Jaguar, American prototype swing-wing fighter aircraft.
- 1951 – First flight of the Fokker S.14 Machtrainer, Dutch two-seater military training jet aircraft.
- 1951 – U. S. Air Force Captain James Jabara becomes the first fighter ace to score his five victories in a jet (an F-86 Sabre) against jets (Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15 s). (This is repeated on 20 May, which is the correct date)
- 1951 – RCAF No. 410 Squadron began re-equipping with North American Sabre fighters. It was the first RCAF squadron to receive this new fighter.
- 1949 – A JRM Mars sets a new record of 308 for the largest number of people to be carried on a single aircraft.
- 1948 – Birth of Jean-Pierre Haigneré, French Air Force officer and former CNES astronaut.
- 1947 – The crash of a Beechcraft C-45F Expeditor, 44-87142, of the 4000th AAF Base Unit, two miles S of Windsor, Ontario, Canada, kills three officers and two enlisted men of the 4140th Base Unit, Wright Field, Ohio, who had departed that base at 1805 hrs. on a flight to Selfridge Field, Michigan, to make advance preparations for air shows throughout the country. The twin-prop, twin-tailed aircraft came down in an open area during a driving rainstorm at ~2105 hrs. and broke into six major pieces. One crew attempted to parachute but was unsuccessful. The plane impacted within 500 yards of St. Mary's academy girls' school on the outskirts of Windsor
- 1947 – First flight of the Cunliffe-Owen Concordia, British twin-engined small airliner.
- 1946 – First flight of the Handley Page Marathon
- 1945 – 29 aircraft from the British aircraft carriers HMS Ameer, HMS Khedive, and HMS Stalker conduct devastating strikes against Japanese shipping, airfields, and communications in southern Burma and Sumatra.
- 1945 – First flight of Tupolev TU-10, a Soviet twin-engine, high speed daylight bomber, an evolution of the TU-2.
- 1944 – American aircraft raid Marcus Island.
- 1943 – Northrop N-9M-1, one-third scale flying testbed for the Northrop XB-35 flying wing design, crashes approximately 12 mi (19 km) W of Muroc Army Air Base, California, killing pilot Max Constant. First flown 27 December 1942, airframe had only logged 22.5 hours, and little data was accumulated before the loss. Post-crash investigation suggested that: "...while Constant was conducting stalls and aft centre of gravity stability tests, aerodynamic forces developed full aft, which were too strong for Constant to overcome, trapping him in the cockpit. To prevent this happening on future flights, a one-shot hydraulic boost device was installed to push the controls forward in an emergency."
- 1942 – RCAF No. 162 (BR) Bomber Reconnaissance Squadron was formed at Yarmouth, Nova Scotia with Canso A aircraft.
- 1939 – Birth of Francis Richard "Dick" Scobee, American astronaut who was killed commanding the Space Shuttle Challenger, which suffered catastrophic booster failure during launch of the STS-51-L mission.
- 1937 – Prototype Sud-Est LeO H-47 flying boat sustains fatigue failure damage to hull bottom on take-off and, upon landing at Antibes at 19,000 kg (42,000 lb), took in water that displaced the centre of gravity, sinking the aircraft.
- 1937 – Entered into service was the Fairey Battle with No. 63 Squadron, Royal Air Force.
- 1934 – First flight of the Russian Tupolev ANT-20 Maxim Gorky, Soviet eight-engine aircraft, at this time the largest aircraft in the world. Capable of carrying 80 passengers, it was used mainly as a mobile propaganda office.
- 1924 – The first aerial circumnavigation of Australia is carried out, by an RAAF crew in a Fairey IIID.
- 1918 – First prototype Sopwith Salamander, E5429, crashes during test program while with No. 65 Squadron when the pilot has to avoid a tender crossing the aerodrome responding to another crash.
- 1918 – Raoul Lufbery, commander of the US 94th Aero Squadron|94th (Hat in the Ring) Aero Squadron and second highest scoring American ace with 17 victories, is killed in air combat.
- 1917 – A Royal Naval Air Service Curtiss H-12 Large America flying boat bombs and sinks the German submarine U-36 in the North Sea near the North Hinder light ship while flying a “Spider Web” patrol. U-36 becomes the only German submarine sunk by an aircraft during World War I. (This is repeated on 20 May)
- 1912 – First official mail flight service of the Deutschen Reichspost between Mannheim and Heidelberg.
- 1910 – Birth of Jean Niland (Aka James Williams), French early parachutist and record setter.
- 1897 – Birth of Frank Luke, Jr., WWI American fighter ace, ranking second among U. S. Army Air Service pilots to Captain Eddie Rickenbacker in number of aerial victories during World War I.
- 1891 – Birth of Oswald Boelcke, WWI German flying ace and one of the most influential patrol leaders and tacticians of the early years of air combat.
- 1886 – Birth of Richard Bell Davies VC, CB, DSO, AFC, British WWI fighter pilot and Royal Navy officer.
References
- "NATO Bombs Gadhafi Warships". MSNBC. 20 May 2011. Retrieved 7 June 2011.
- "Marine Deaths in Iraq, Marines killed in Action, May 18–19, 2003". Retrieved 2007-07-31.
- Shortcuts to this page: Portal:Airplanes • P:AVIA













%252C_Netherlands_PP1151411024_(cropped).jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)



.png.webp)


.jpg.webp)




.jpg.webp)
















.jpg.webp)





.jpg.webp)