Portal:Solar System
The Solar System Portal

The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit the star. The largest of such objects are the eight planets, in order from the Sun: four terrestrial planets named Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, two gas giants named Jupiter and Saturn, and two ice giants named Uranus and Neptune. The terrestrial planets have a definite surface and are mostly made of rock and metal. The gas giants are mostly made of hydrogen and helium, while the ice giants are mostly made of 'volatile' substances such as water, ammonia, and methane. In some texts, these terrestrial and giant planets are called the inner Solar System and outer Solar System planets respectively.
The Solar System was formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. Over time, the cloud formed the Sun and a protoplanetary disk that gradually coalesced to form planets and other objects. That is the reason why all eight planets have an orbit that lies near the same plane. In the present day, 99.86% of the Solar System's mass is in the Sun and most of the remaining mass is contained in the planet Jupiter. Six planets, six largest possible dwarf planets and many other bodies have natural satellites or moons orbiting around them. All giant planets and a few smaller bodies are encircled by planetary rings, composed of ice, dust and sometimes moonlets.
There are an unknown number of smaller dwarf planets and innumerable small bodies orbiting the Sun. These objects are distributed in the asteroid belt that lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, the Kuiper belt, the scattered disc that both lies beyond Neptune's orbit and at even further reaches of the Solar System which they would be classified as an extreme trans-Neptunian object. There is consensus among astronomers to these nine objects as dwarf planets: the asteroid Ceres, the Kuiper-belt objects Pluto, Orcus, Haumea, Quaoar, and Makemake, and the scattered-disc objects Gonggong, Eris, and Sedna. Many small-body populations, including comets, centaurs and interplanetary dust clouds, freely travel between the regions of the Solar System.
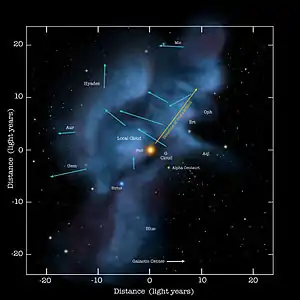
The solar wind, a stream of charged particles flowing outwards from the Sun, creates a bubble-like region of the interplanetary medium in the interstellar medium known as the heliosphere. The heliopause is the point at which pressure from the solar wind is equal to the opposing pressure of the interstellar medium; it extends out to the edge of the scattered disc. The Oort cloud, which is thought to be the source for long-period comets, may also exist at a distance roughly a thousand times further than the heliosphere. The nearest stars to the Solar System are within the Local Bubble; the closest star is named Proxima Centauri and is at a distance of 4.2441 light-years away. (Full article...)
Selected article –

According to current theories, Mercury may have a solid silicate crust and mantle overlying a solid outer core, a deeper liquid core layer, and a solid inner core. Having almost no atmosphere to retain heat, Mercury has surface temperatures that change wildly during the day, ranging from 100 K (−173 °C; −280 °F) at night to 700 K (427 °C; 800 °F) during sunlight across the equator regions. At Mercury's poles though, there are large reservoirs of water ices that are never exposed to direct sunlight, which has an estimated mass of about 0.025–0.25% the Antarctic ice sheet. There are many competing hypothesis about Mercury's origins and development, some of which incorporate collision with planetesimal and rock vaporization.
Because Mercury is very close to the Sun, the intensity of sunlight on its surface is between 4.59 and 10.61 times the solar constant (amount of the Sun's energy received at 1 astronomical unit, which is roughly the distance between Earth and the Sun). Mercury orbits the Sun in a 3:2 spin–orbit resonance, meaning that relative to the background stars, it rotates on its axis exactly three times for every two revolutions it makes around the Sun. Counterintuitively, due to Mercury's slow rotation, an observer on the planet would see only one Mercurian solar day (176 Earth days) every two Mercurian solar years (88 Earth days each). Mercury's axis has the smallest tilt of any of the Solar System's planets (about 1⁄30 of a degree), and its orbital eccentricity is the largest of all known planets in the Solar System. (Full article...)
Selected picture
General images
The following are images from various Solar System-related articles on Wikipedia.
Did you know –

- ...that New York's Panther Mountain (pictured) was the site of a prehistoric meteor crash?
- ...that the Beethoven crater in the Beethoven quadrangle on Mercury is the eleventh largest named impact crater in the Solar System?
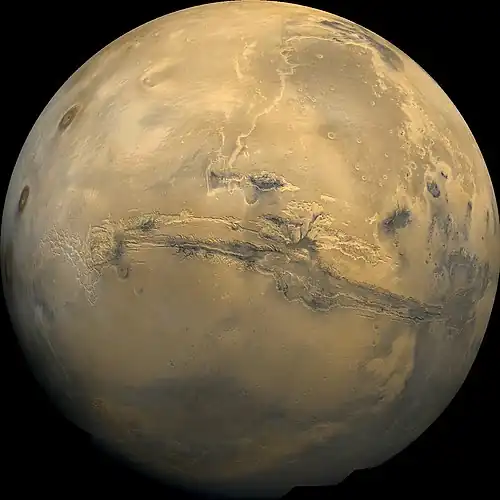
- ...that the planet Mars appears red primarily because of a ubiquitous layer of dust containing nanophase ferric oxides?
- ...that the 1997 volcanic eruption of Pillan Patera on Jupiter's moon Io was the largest effusive eruption ever witnessed?
- ...that ridges and escarpments in the Victoria quadrangle of the planet Mercury have been associated with the stresses caused by the Sun slowing Mercury's rotation through tidal forces?
- ...that J002E3 was at first thought to be a new moon of Earth when discovered in 2002 but was later found to be the third stage of the Apollo 12 Saturn V?
- ...that the Tooting impact crater on Mars was named after the London suburb of the same name because the discoverer "thought [his] mum and brother would get a kick out of having their home town paired with a land form on Mars"?
- ...that 99% of the mass of the Carme group, a group of retrograde irregular satellites of Jupiter, is located in Carme?
Categories
| Solar System | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
||
| Celestial mechanics | Comets | ...in fiction |
 |
 | |
| Minor planets | Moons | Planetary missions |
 |
 |
.jpg.webp) |
| Planets... | Sun | Surface feature nomenclature... |
In the news
- April 7: NASA's helicopter Ingenuity survives its first night at Mars
- December 25: 'Earth-based life can survive in hydrogen-rich atmospheres': MIT professor Dr Seager tells Wikinews about her research on organisms thriving in oxygen-less environment
- July 7: Astronomer Anthony Boccaletti discusses observation of birth of potential exoplanet with Wikinews
- May 31: SpaceX successfully launches its first crewed spaceflight
- May 22: Astronomer tells Wikinews about discovery of closest black hole known so far
- October 12: Cosmonaut Alexei Leonov dies at age 85
- October 10: Swedish academy announces 2019 Nobel Prize winners in physics
- September 14: Astronomers find water vapour in atmosphere of exoplanet K2-18b
- March 5: SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule docks with International Space Station
- January 9: Simple animals could live in Martian brines: Wikinews interviews planetary scientist Vlada Stamenković
- November 29: NASA's InSight Lander makes it to Mars
- October 12: Manned Soyuz space mission aborts during launch
Major topics
Solar System: Planets (Definition · Planetary habitability · Terrestrial planets · Gas giants · Rings) · Dwarf planets (Plutoid) · Colonization · Discovery timelineˑ Exploration · Moons · Planetariums
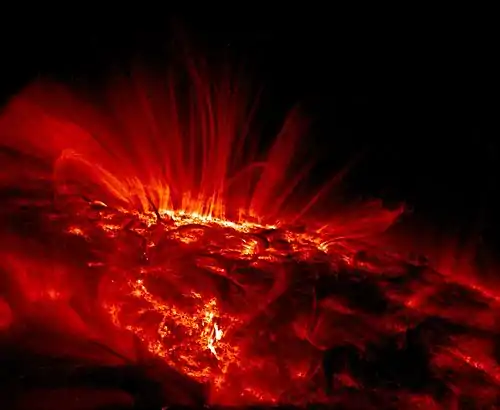
- Sun: Sunspot · Solar wind · Solar flare · Solar eclipse
- Mercury: Geology · Exploration (Mariner 10 · MESSENGER · BepiColombo) · Transit
- Venus: Geology · Atmosphere · Exploration (Venera · Mariner program 2/5/10 · Pioneer · Vega 1/2ˑ Magellan · Venus Express) · Transit
- Earth: History · Geology · Geography · Atmosphere · Rotation
- Moon: Geology · Selenography · Atmosphere · Exploration (Luna · Apollo 8/11) · Orbit · Lunar eclipse
- Mars: Moons (Phobos · Deimos) · Geology · Geography · Atmosphere · Exploration (Mariner · Mars · Viking 1/2 · Pathfinder · MER)
- Ceres: Exploration (Dawn)
- Jupiter: Moons (Amalthea, Io · Europa · Ganymede · Callisto) · Rings · Atmosphere · Magnetosphere · Exploration (Pioneer 10/11 · Voyager 1/2 · Ulysses · Cassini · Galileo · New Horizons)
- Saturn: Moons (Mimas · Enceladus · Tethys · Dione · Rhea · Titan · Iapetus) · Rings · Exploration (Pioneer 11 · Voyager 1/2 · Cassini–Huygens)
- Uranus: Moons (Miranda · Ariel · Umbriel · Titania · Oberon) · Rings · Exploration (Voyager 2)
- Neptune: Moons (Triton) · Rings · Exploration (Voyager 2)
- Planets beyond Neptune
- Pluto: Moons (Charon, Nix, Hydra, Kerberos, Styx) · Exploration (New Horizons)
- Haumea: Moons (Hi'iaka, Namaka)
- Makemake
- Eris: Dysnomia
- Small bodies: Meteoroids · Asteroids (Asteroid belt) · Centaurs · TNOs (Kuiper belt · Scattered disc · Oort cloud) · Comets (Hale–Bopp · Halley's · Hyakutake · Shoemaker–Levy 9)
- Formation and evolution of the Solar System: History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses · Nebular hypothesis
- See also: Featured content · Featured topic · Good articles · List of objects
Bold articles are featured.
Italicized articles are on dwarf planets or major moons.
Things you can do

 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Related portals
Related WikiProjects
 |
 | |
| Solar System | Moon | Mars |
|---|---|---|
 |
 | |
| Astronomy | Astronomical objects | Spaceflight |
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals





























.jpg.webp)

















.jpg.webp)