Submersible bridge
A submersible bridge is a type of movable bridge that lowers the bridge deck below the water level to permit waterborne traffic to use the waterway. This differs from a lift bridge or table bridge, which operate by raising the roadway. Two submersible bridges exist across the Corinth Canal in Greece, one at each end, in Isthmia and Corinth.[1] They lower the centre span to 8 metres below water level when they give way to ships crossing the channel. The bridges are 33 meters long, 7 meters wide and have 2 traffic lanes.[2] Their vertical sinking speed is 4 meters per minute; therefore, the sinking or refloating procedure lasts around 3 and a half minutes in total, however due to the policy of only sinking the bridges when a ship is due to pass through the canal means the safety procedure begins 15 minutes before the ship approaches.
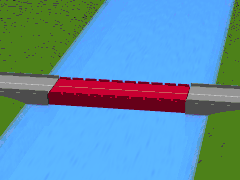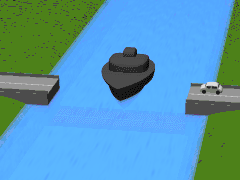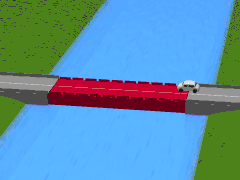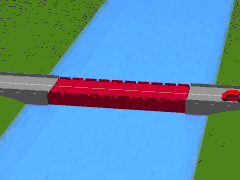 Submerging | |
| Ancestor | Plate girder bridge, |
|---|---|
| Related | Lift bridge, bascule bridge, table bridge |
| Descendant | None |
| Carries | Automobile, pedestrians |
| Span range | Short |
| Material | Steel |
| Movable | Yes |
| Design effort | Medium |
| Falsework required | No |
The submersible bridge's primary advantage over the similar lift bridge is that there is no structure above the shipping channel and thus no height limitation on ship traffic. This is particularly important for sailing vessels. Additionally, the lack of an above-deck structure is considered aesthetically pleasing, a similarity shared with the Chicago-style bascule bridge and the table bridge. However, the presence of the submerged bridge structure limits the draft of vessels in the waterway.
The term submersible bridge is also sometimes applied to a non-movable bridge that is designed to withstand submersion and high currents when the water level rises. Such a bridge is more properly called a low water bridge.

See also
- Low water crossing, a non-moving bridge that is sometimes submerged
- Moveable bridges for a list of other moveable bridge types
- Table bridge, a similar bridge that moves upward
- Underwater bridge, a non-moving military bridge that is always submerged
References
- Moore, Richard (February 1990). Fodor's 90 Greece. Fodor's Travel Publications. p. 152. ISBN 9780679017721.
- "Posidonia Submersible Bridge | Bridges".
External links
- Popular Science, November 1943, "Ducking Bridge" Lowers Span To Allow Ships To Pass built in Iraq in 1943 (bottom-right hand side of page)
- Video of the operation of a submersible bridge at the entrance of the Corinth Canal
