Anterior cardiac veins
The anterior cardiac veins (or anterior veins of right ventricle) are a variable number of small veins (usually 2-5)[1] which drain blood from the anterior portion of the right ventricle into the right atrium.[1][2]
| Anterior cardiac veins | |
|---|---|
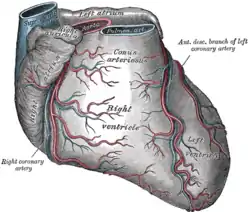 Sternocostal surface of heart. (Anterior cardiac veins not labeled, but visible at left.) | |
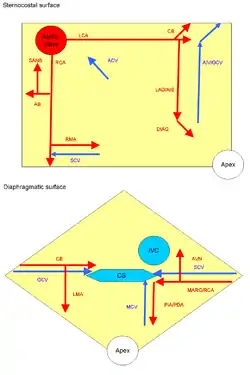 Arteries: RCA = right coronary AB = atrial branches SANB = sinuatrial nodal RMA = right marginal LCA = left coronary CB = circumflex branch LAD/AIB = anterior interventricular LMA = left marginal PIA/PDA = posterior descending AVN = atrioventricular nodal Veins: SCV = small cardiac ACV = anterior cardiac AIV/GCV = great cardiac MCV = middle cardiac CS = coronary sinus | |
| Details | |
| Drains to | Right atrium |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | venae cardiacae anteriores, venae ventriculi dextri anteriores |
| TA98 | A12.3.01.012 |
| TA2 | 4168 |
| FMA | 71567 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Anatomy
The right marginal vein frequently opens into the right atrium,[1] and is therefore sometimes regarded as belonging to this group.
Fate
Unlike most cardiac veins, the anterior cardiac veins do not end in the coronary sinus; instead, they drain directly into[2] the anterior wall of the right atrium.[2]
References
- Standring, Susan (2016). Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice (41 ed.). Elsevier Limited. pp. 994–1023. ISBN 978-0-7020-5230-9.
- Morton, David A. (2019). The Big Picture: Gross Anatomy. K. Bo Foreman, Kurt H. Albertine (2nd ed.). New York. p. 52. ISBN 978-1-259-86264-9. OCLC 1044772257.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.