Central tegmental tract
The central tegmental tract[1] is a structure in the midbrain and pons.
| Central tegmental tract | |
|---|---|
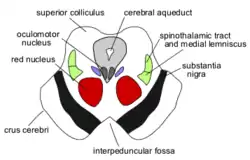 Diagram of the midbrain, sectioned at the level of the superior colliculus (Central tegmental tract not labeled, but region is visible.) | |
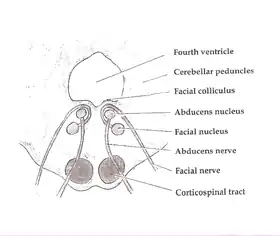 Axial section of the Brainstem (Pons) at the level of the Facial Colliculus (Central tegmental tract not labeled, but region is visible.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Tractus tegmentalis centralis |
| NeuroNames | 2204 |
| TA98 | A14.1.05.325 |
| TA2 | 5869 |
| FMA | 83850 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
It contains:
- ascending axonal fibers that arise from the rostral nucleus solitarius and terminate in the ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM) of thalamus. Information from the thalamus will go to cortical taste area, namely the insula and frontal operculum.
- descending rubroolivary fibers arising from the parvocellular red nucleus to terminate in the ipsilateral inferior olivary nucleus.[2]: 292, 298 This latter pathway (the rubro-olivary tract) will be used to connect the contralateral cerebellum.
- ascending[2]: 306 reticulothalamic fibres[2]: 112 projecting from the medial zone nuclei of the reticular formation to the hypothalamus (to mediate autonomic nervous system response), and the intralaminar thalamic nuclei[2]: 306 (to mediate a startle response to pain[2]: 112 ).
Clinical significance
Lesion of the tract can cause palatal myoclonus, e.g. in myoclonic syndrome, in strokes of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery.
Additional Images
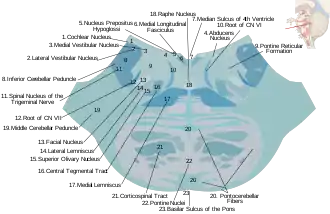 Horizontal section through the lower part of the pons. The central tegmental tract is labeled #16.
Horizontal section through the lower part of the pons. The central tegmental tract is labeled #16.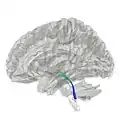 Tractography showing central tegmental tract
Tractography showing central tegmental tract
References
- Kamali A, Kramer LA, Butler IJ, Hasan KM. Diffusion tensor tractography of the somatosensory system in the human brainstem: initial findings using high isotropic spatial resolution at 3.0 T. Eur Radiol. 2009 19:1480-8. doi: 10.1007/s00330-009-1305-x. PMID 19189108
- Patestas, Maria A.; Gartner, Leslie P. (2016). A Textbook of Neuroanatomy (2nd ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-118-67746-9.
External links
- Midbrain at Inferior Colliculus - IV Nucleus, Sectional Atlas
- Mid Pons at the Trigeminal Motor Nucleus, Sectional Atlas
- Neuroanatomy / plate12, Frank Willard
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.