Columbia Mountains
The Columbia Mountains are a group of mountain ranges along the Upper Columbia River in British Columbia, Montana, Idaho and Washington. The mountain range covers 135,952 km² (52,491 sq mi). The range is bounded by the Rocky Mountain Trench on the east, and the Kootenai River on the south; their western boundary is the edge of the Interior Plateau. Seventy-five percent of the range is located in Canada and the remaining twenty-five percent in the United States; American geographic classifications place the Columbia Mountains as part of the Rocky Mountains complex, but this designation does not apply in Canada (despite a British Columbia government tourism campaign to rebrand their southern portion as the "Kootenay Rockies"). Mount Sir Sandford is the highest mountain in the range, reaching 3,519 metres (11,545 ft).
| Columbia Mountains | |
|---|---|
 Mount Sir Sandford from the Gothics Glacier | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Mount Sir Sandford |
| Elevation | 3,519 m (11,545 ft) |
| Coordinates | 51°39′24″N 117°52′03″W |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 741 km (460 mi) N-S |
| Width | 493 km (306 mi) W-E |
| Area | 135,952 km2 (52,491 sq mi) |
| Geography | |
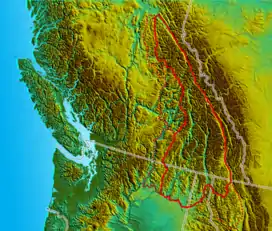 Location map of Columbia Mountains: dotted lines to left mark boundaries of Okanagan, Shuswap and Quesnel Highlands, dotted lines to lower right mark Salish and Cabinet Mountains.
| |
| Countries | Canada and United States |
| Provinces/States | British Columbia, Idaho, Montana and Washington |
| Parent range | North American Cordillera |

Mountain ranges
The Columbia Mountains are made up of four large ranges containing many subranges:
- Cariboo Mountains
- Lunn Icefield
- Mowdish Range
- Premier Range
- Vimy Ridge
- Wavy Range
- Monashee Mountains
- Anstey Range
- Christina Range
- Gold Range
- Jordan Range
- Kettle River Range
- Malton Range
- Midway Range
- Ratchford Range
- Rossland Range
- Scrip Range
- Whatshan Range
- The Pinnacles
- Selkirk Mountains
- Asulkan Range
- Battle Range
- Big Bend Ranges
- Adamant Range
- Sir Sandford Range
- Windy Range
- Bishops Range
- Bonnington Range
- Clachnacudainn Range
- Dawson Range
- Duncan Ranges
- Badshot Range
- Goat Range
- Hermit Range
- Kokanee Range
- Slocan Ranges
- Lardeau Range
- Nelson Range
- Purity Range
- Sir Donald Range
- Valhalla Ranges
- Ruby Range
- Valkyr Range
- Norns Range
- Purcell Mountains (Percell Mountains in the United States)
- The Bugaboos Group
- Carbonate Range
- Dogtooth Range
- Farnham Group
- MacBeth Group
- McGillivary Range
- Moyie Range
- Septet Range
- Spillimacheen Range
- Starbird Ridge
- Commander Group
- Stockdale Group
- Toby Glacier
- Truce Group
- Yahk Range
Additionally lower areas to the west of the main ranges are sometimes included in the description of the Cariboo Mountains:
- Quesnel Highland
- Gosse Range
- Palmer Range
- Goose Range
- Palmer Range
- Shuswap Highland
- Hunters Range
- Mabel Range
- Park Range
- Sawtooth Range
- Seymour Range
- Shuswap Range
- Silver Hills
- Trinity Hills
- Okanagan Highland
- Beaverdell Range
Some classification systems end the Columbia Mountains at the North Thompson River, such that the Cariboo Mountains are assigned to the Interior Plateau. Where the Columbia Mountains meet the Interior Plateau there are intermediary areas known as highlands - the Quesnel Highland (west flank of the Cariboos), the Shuswap Highland (south of the Cariboos and west of the northern Monashees), and the Okanagan Highland (west of the southern Monashees). These are listed here but are often considered to be part of the Interior Plateau.
Some geographic classifications also include the Cabinet Mountains and Salish Mountains, which lie south of the Purcells between the Kootenai River and the Clark Fork of the Columbia, but in US classification systems they are generally considered to be part of the Rocky Mountains.
Physiographically, they are a distinct province of the larger Rocky Mountain System physiographic division.
Highest Mountains
The following mountains are the 10 highest mountains (in order) contained within the Columbian Mountains:"Columbia Mountains". Peakbagger.com.
- Mount Sir Sandford (3,519 m) (Selkirks)
- Mount Sir Wilfrid Laurier (3,516 m) (Cariboos)
- Mount Farnham (3,493 m) (Purcells)
- Jumbo Mountain (3,437 m) (Purcells)
- Howser Spire (3,412 m) (Purcells)
- Mount Delphine (3,406 m) (Purcells)
- Mount Sir John Abbott (3,398 m) (Cariboos)
- Mount Hammond (3,387 m) (Purcells)
- Mount Dawson (3,377 m) (Selkirks)
- Eyebrow Peak (3,362 m) (Purcells)
Passes
The following passes are located within or on the perimeter of the Columbia Mountains:
- Cedarside Pass (Fraser and Columbia Rivers 800m)
- Canal Flats (Columbia and Kootenay Rivers)
- Rogers Pass (between Revelstoke and Golden)
- Kootenay Pass (between Trail and Creston)
- Eagle Pass (between Revelstoke and Sicamous)
- Monashee Pass (BC Hwy 6)
- Bonanza Pass (Christina Lake to Castlegar/Rossland)
National and provincial parks

- Ansty Hunakwa Protected Area
- Bowron Lake Provincial Park
- Bugaboo Provincial Park
- Cariboo Mountains Provincial Park
- Dunn Peak Protected Area
- Glacier National Park
- Gladstone Provincial Park
- Goat Range Provincial Park
- Granby Provincial Park
- Graystokes Provincial Park
- Kianuko Provincial Park
- Kokanee Glacier Provincial Park
- Monashee Provincial Park
- Mount Revelstoke National Park
- Myra-Bellevue Provincial Park
- Okanagan Mountain Provincial Park
- Purcell Wilderness Conservancy Provincial Park and Protected Area
- St. Mary's Alpine Provincial Park
- Silver Star Provincial Park
- Valhalla Provincial Park
- Wells Gray Provincial Park
- West Arm Provincial Park
- West Twin Provincial Park and Protected Area
See also
 Pacific Northwest portal
Pacific Northwest portal
