Ethotoin
Ethotoin (previously marketed as Peganone) is an anticonvulsant drug used in the treatment of epilepsy.[1] It is a hydantoin, similar to phenytoin. It is not available in the United States.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a682022 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 3–9 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.514 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H12N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 204.229 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of ethotoin is similar to that of phenytoin.
Approval history
- 1957 Peganone was granted Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval to Abbott Laboratories for treatment of grand mal (tonic clonic) and partial complex (psychomotor) seizures.
- 2003 Peganone was acquired from Abbott Laboratories by Ovation Pharmaceuticals (specialty pharmaceutical company who acquire underpromoted branded pharmaceutical products).
- 2018 It was announced by Recordati Rare Diseases Inc. that due to a combination of low product demand and complex manufacturing difficulties, product manufacturing, distribution and sale was being discontinued.
Indications and usage
Ethotoin is indicated for tonic-clonic and partial complex seizures.[2]
Dosing
Ethotoin is available in 250 mg tablets.[3][4] It is taken orally in 4 to 6 divided doses per day, preferably after food.
Side effects
Side effects include ataxia, visual disturbances, rash, and gastrointestinal problems.
Chemistry
Ethotoin is synthesized by the reaction of benzaldehyde oxynitrile (2) with urea or ammonium bicarbonate, which forms an intermediate urea derivative (3) which on acidic conditions cyclizes to 5-phenylhydantoin (4).[5] Alkylation of this product using ethyl iodide leads to the formation of ethotoin (5).
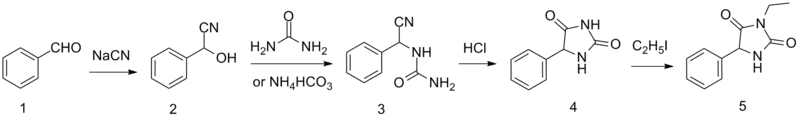 Synthesis of ethotoin
Synthesis of ethotoin
References
- Schwade ED, Richards RK, Everett GM (May 1956). "Peganone, a new antiepileptic drug". Dis Nerv Syst. 17 (5): 155–8. PMID 13317788.
- Shorvon, S.D.; Fish, David R.; Perucca, Emilio; Dodson, W. Edwin, eds. (2004). The Treatment of Epilepsy. Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 0-632-06046-8.
- "Ethotoin". drugs.com.
- "PEGANONE 250 mg Ethotoin Tablets, USP" (PDF).
- A. Pinner, Chem. Ber., 21, 2324 (1888); W.J. Close, U.S. patent 2,793,157 (1946)