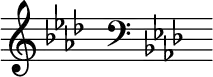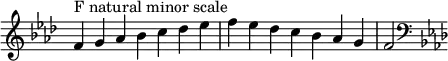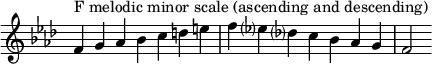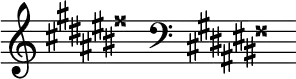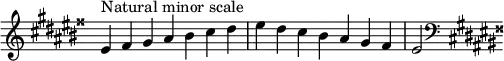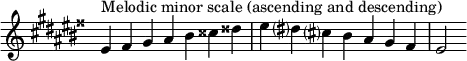F minor
F minor is a minor scale based on F, consisting of the pitches F, G, A♭, B♭, C, D♭, and E♭. Its key signature consists of four flats. Its relative major is A-flat major and its parallel major is F major. Its enharmonic equivalent, E-sharp minor, has six sharps and the double sharp F![]() , which makes it impractical to use.
, which makes it impractical to use.
| Relative key | A-flat major |
|---|---|
| Parallel key | F major |
| Dominant key | C minor |
| Subdominant | B-flat minor |
| Component pitches | |
| F, G, A♭, B♭, C, D♭, E♭ | |
Scale and scale-degree chords
The F natural minor scale is
Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The F harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are
The scale-degree chords of F minor are:
- Tonic – F minor
- Supertonic – G diminished
- Mediant – A-flat major
- Subdominant – B-flat minor
- Dominant – C minor
- Submediant – D-flat major
- Subtonic – E-flat major
Music in F minor
Famous pieces in the key of F minor include Beethoven's Appassionata Sonata, Chopin's Piano Concerto No. 2, Ballade No. 4, Haydn's Symphony No. 49, La Passione and Tchaikovsky’s Symphony No. 4.
Glenn Gould once said if he could be any key, he would be F minor, because "it's rather dour, halfway between complex and stable, between upright and lascivious, between gray and highly tinted... There is a certain obliqueness."[1]
Hermann von Helmholtz once described F minor as harrowing and melancholy. Christian Schubart described this key as "Deep depression, funereal lament, groans of misery and longing for the grave".[2]
Notable compositions
- Giovanni Battista Pergolesi
- Stabat Mater
- Antonio Vivaldi
- "Winter" from The Four Seasons, RV 297
- Johann Sebastian Bach
- Harpsichord Concerto No. 5
- "Ich ruf zu dir, Herr Jesu Christ", BWV 639
- Joseph Haydn
- Symphony No. 49 ("La Passione")
- Variations in F minor
- Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
- Aria "L'ho perduta, me meschina" from The Marriage of Figaro, act 4
- Adagio and Allegro in F minor for a mechanical organ, K. 594
- Jan Ladislav Dussek
- Piano Sonata No. 28 in F minor "L'invocation", Op. 77
- Ludwig van Beethoven
- Egmont, Op. 84: Overture in F minor
- Piano Sonata No. 1, Op. 2/1
- Piano Sonata No. 23 (Appassionata), Op. 57
- String Quartet No. 11 "Serioso", Op. 95
- Felix Mendelssohn
- String Quartet No. 6
- Organ Sonata, Op. 65, No. 1
- Carl Maria von Weber
- Clarinet Concerto No. 1
- Konzertstück in F minor
- Frédéric Chopin
- Ballade No. 4, Op. 52
- Fantaisie in F minor, Op. 49
- Trois nouvelles études, No. 1
- Étude Op. 10, No. 9
- Étude Op. 25, No. 2 "Bees"
- Prelude Op. 28, No. 18 "Suicide"
- Piano Concerto No. 2, Op. 21
- Nocturne in F minor, Op. 55 No. 1
- Mazurka, Op. 63 No. 2
- Mazurka, Op. 68 No. 4 (Posthumous)
- Charles-Valentin Alkan
- Prelude, Op. 31, No. 2 (Assez lentement)
- Symphony for Solo Piano, 2nd movement: Marche funèbre
- Franz Liszt
- Funérailles
- Transcendental Étude No. 10 "Appassionata"
- Trois études de concert, No. 2 "La leggierezza"
- Franz Schubert
- Fantasia in F minor
- Impromptu No. 1, Op. 142
- Impromptu No. 4, Op. 142
- Robert Schumann
- Piano Sonata No. 3
- Johannes Brahms
- Piano Quintet, Op. 34
- Piano Sonata No. 3, Op. 5
- Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
- Symphony No. 4
- The Tempest
- Anton Bruckner
- Mass No. 3
- Alexander Borodin
- String Quintet
- Paul Dukas
- Ralph Vaughan Williams
- English Folk Songs
- Symphony No. 4
- Tuba Concerto in F minor
- Dmitri Shostakovich
- Symphony No. 1
- String Quartet No. 11, Op. 122
- Johann Pachelbel
- Chaconne in F minor
E-sharp minor
| Relative key | G-sharp major (theoretical) →enharmonic: A-flat major |
|---|---|
| Parallel key | E-sharp major (theoretical) →enharmonic: F major |
| Dominant key | B-sharp minor (theoretical) →enharmonic: C minor |
| Subdominant | A-sharp minor |
| Enharmonic | F minor |
| Component pitches | |
| E♯, F | |
E-sharp minor is a theoretical key based on the musical note E♯, consisting of the pitches E♯, F![]() , G♯, A♯, B♯, C♯ and D♯. Its key signature has one double sharp and six sharps (or eight sharps). Its relative major is G-sharp major, which is usually replaced by A-flat major. Its parallel major, E-sharp major, is usually replaced by F major, as E-sharp major’s four double-sharps make it impractical to use. It's enharmonic minor is F minor whose key signature has four flats. Because of that enharmonic relationship, it is usually noted as the enharmonic equivalent of F minor instead of E-sharp minor.
, G♯, A♯, B♯, C♯ and D♯. Its key signature has one double sharp and six sharps (or eight sharps). Its relative major is G-sharp major, which is usually replaced by A-flat major. Its parallel major, E-sharp major, is usually replaced by F major, as E-sharp major’s four double-sharps make it impractical to use. It's enharmonic minor is F minor whose key signature has four flats. Because of that enharmonic relationship, it is usually noted as the enharmonic equivalent of F minor instead of E-sharp minor.
The E-sharp natural minor scale is:
Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The E-sharp harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are:
Although E-sharp minor is usually notated as F minor, it could be used on a local level, such as bars 17 to 22 in Johann Sebastian Bach's The Well-Tempered Clavier, Book 1, Prelude and Fugue No. 3 in C-sharp major. (E-sharp minor is the mediant minor key of C-sharp major.)
The scale-degree chords of E-sharp minor are:
- Tonic – E-sharp minor
- Supertonic – F-double-sharp diminished
- Mediant – G-sharp major
- Subdominant – A-sharp minor
- Dominant – B-sharp minor
- Submediant – C-sharp major
- Subtonic – D-sharp major
Notes
- Cathering Meng, Tonight's the Night (Apostrophe Books, 2007): 21
- "Musical Key Characteristics".
External links
 Media related to F minor at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to F minor at Wikimedia Commons