Uridine diphosphate glucose
Uridine diphosphate glucose (uracil-diphosphate glucose, UDP-glucose) is a nucleotide sugar. It is involved in glycosyltransferase reactions in metabolism.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Uridine 5′-(α-D-glucopyranosyl dihydrogen diphosphate) | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O1-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2,4-Dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl} O3-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl] dihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Other names
UDP-glucose | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.657 |
| MeSH | Uridine+Diphosphate+Glucose |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H24N2O17P2 | |
| Molar mass | 566.302 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Functions
UDP-glucose is used in nucleotide sugar metabolism as an activated form of glucose, a substrate for enzymes called glucosyltransferases.[1]
UDP-glucose is a precursor of glycogen and can be converted into UDP-galactose and UDP-glucuronic acid, which can then be used as substrates by the enzymes that make polysaccharides containing galactose and glucuronic acid.
UDP-glucose can also be used as a precursor of sucrose, lipopolysaccharides and glycosphingolipids.
Components
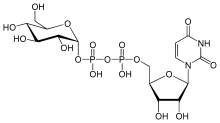
UDP-glucose consists of the pyrophosphate group, ribose, glucose, and uracil.
See also
- DNA
- Nucleoside
- Nucleotide
- Oligonucleotide
- RNA
- TDP-glucose
- Uracil
- Uridine diphosphate
References
- Rademacher T, Parekh R, Dwek R (1988). "Glycobiology". Annu Rev Biochem. 57: 785–838. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004033. PMID 3052290.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.