

/en/googlespreadsheets/converting-and-printing-docs/content/
Google Sheets allows you to organize, edit, and analyze different types of information using spreadsheets. In this lesson, you'll learn about the different ways you might use spreadsheets and how to navigate the Google Sheets interface. You'll also learn the basic ways to work with cells and cell content, including how to select cells, insert content, and copy and paste cells.
Watch the video below to see an overview of Google Sheets.
Google Sheets is a web-based spreadsheet application that allows you to store and organize different types of information, much like Microsoft Excel. While Google Sheets does not offer all of Excel's advanced features, it's easy to create and edit spreadsheets ranging from the simple to the complex.
While you might think spreadsheets are only used by certain people to process complicated numbers and data, they can actually be used for a variety of everyday tasks. Whether you're starting a budget, planning a garden, or creating an invoice or just about anything else you can think of, spreadsheets are a great way to organize information.
Review the slideshow below to learn some of the other ways you might use spreadsheets.
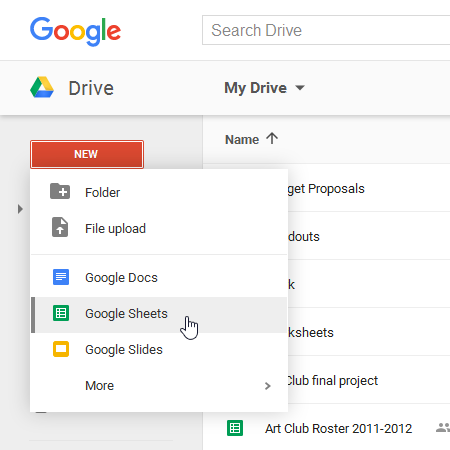
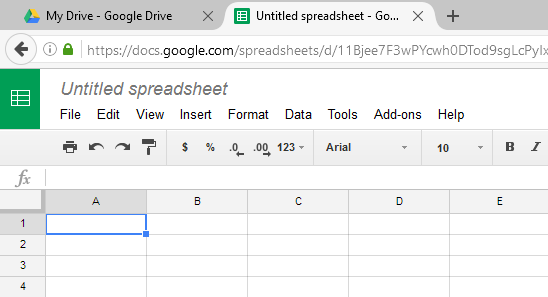
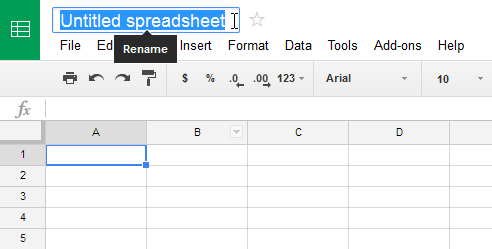
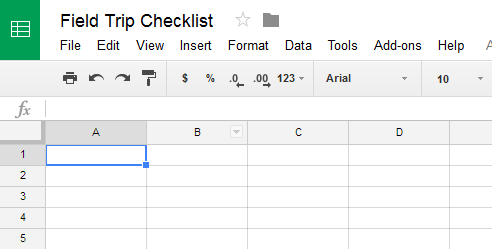
In order to use and edit spreadsheets, you will need to become familiar with the Google Sheets interface.
Click the buttons in the interactive below to learn more about the Google Sheets interface.
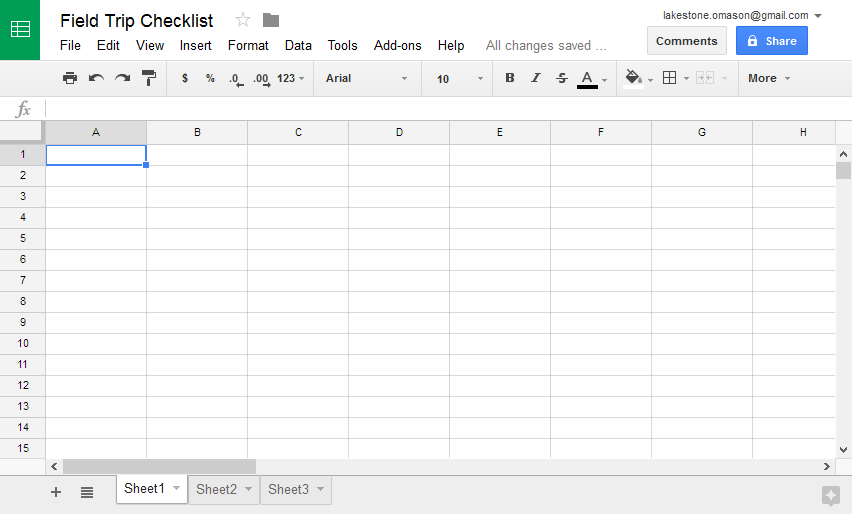
Every spreadsheet is made up of thousands of rectangles, which are called cells. A cell is the intersection of a row and a column. Columns are identified by letters (A, B, C), while rows are identified by numbers (1, 2, 3).
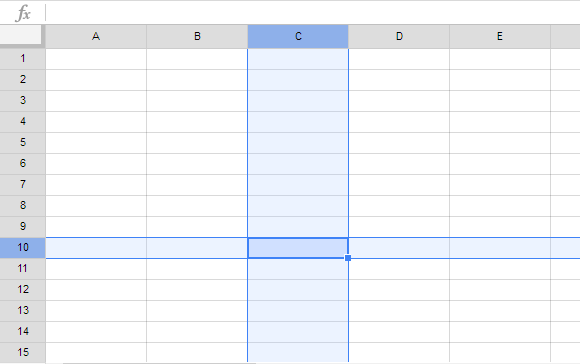
Each cell has its own name—or cell address—based on its column and row. In this example, the selected cell intersects column C and row 10, so the cell address is C10. Note that a cell's column and row headings become darker when the cell is selected.
You can also select multiple cells at the same time. A group of cells is known as a cell range. Rather than a single cell address, you'll refer to a cell range using the cell address of the first and last cells in the cell range, separated by a colon. For example, a cell range that included cells A1, A2, A3, A4, and A5 would be written as A1:A5.
In the images below, two different cell ranges are selected:

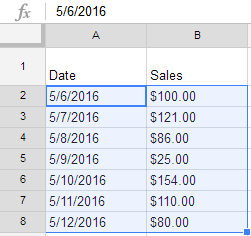
Any information you enter into a spreadsheet will be stored in a cell. Each cell can contain several different types of content, including text, formatting, formulas, and functions.


To input or edit cell content, you'll first need to select the cell.
You can also select cells using the arrow keys on your keyboard.
Sometimes you may want to select a larger group of cells, or cell range.
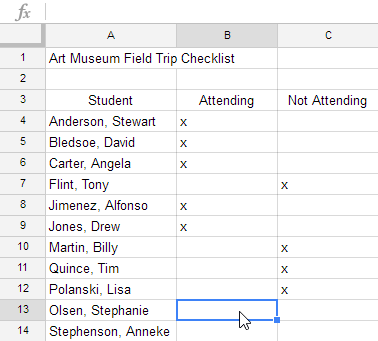
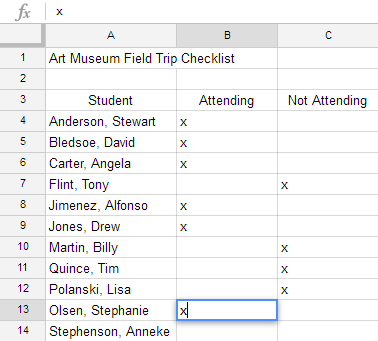
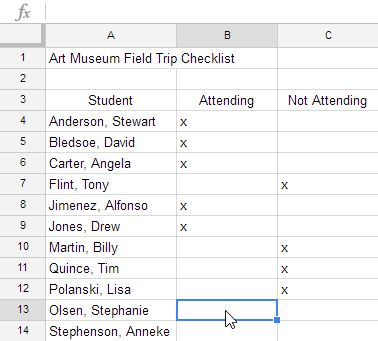
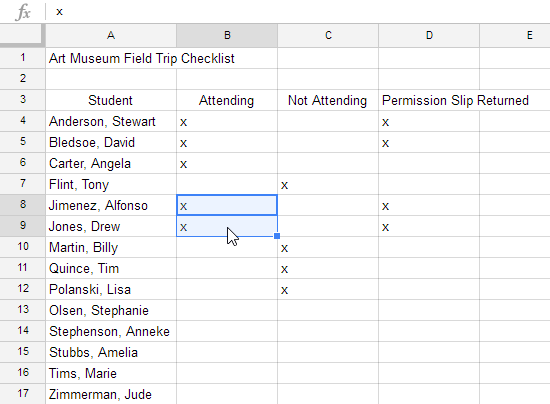
It's easy to copy content that is already entered into your spreadsheet and paste this content to other cells.
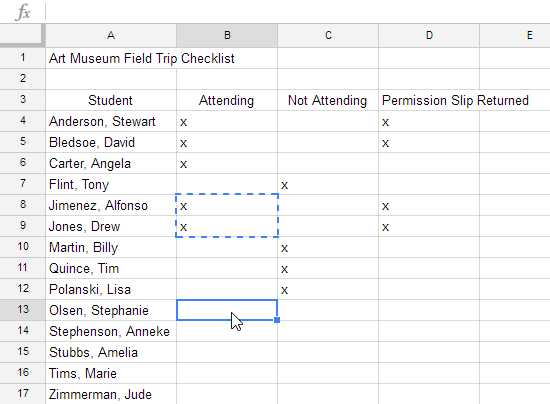
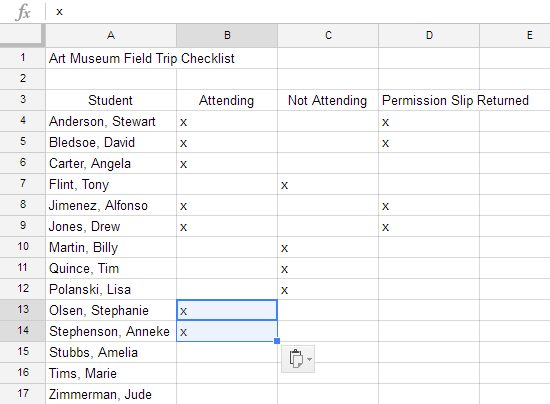
Unlike copying and pasting—which duplicates cell content—cutting and pasting moves content between cells.
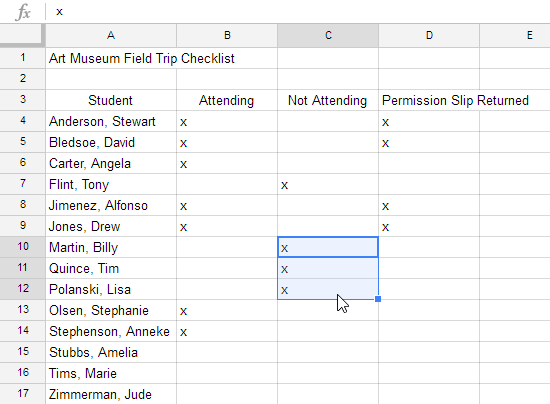
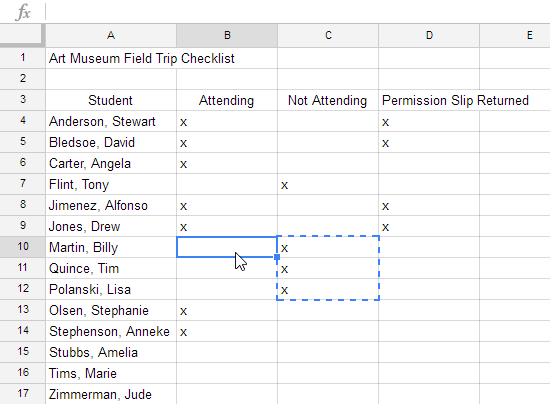
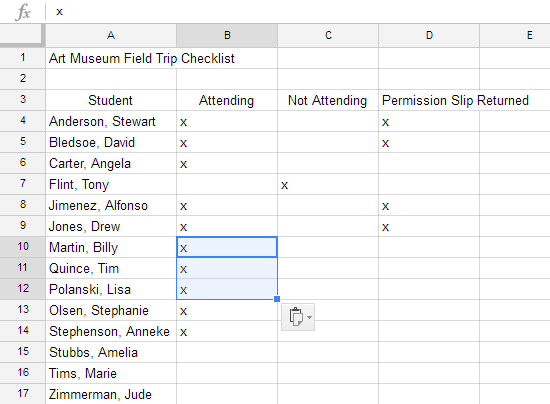
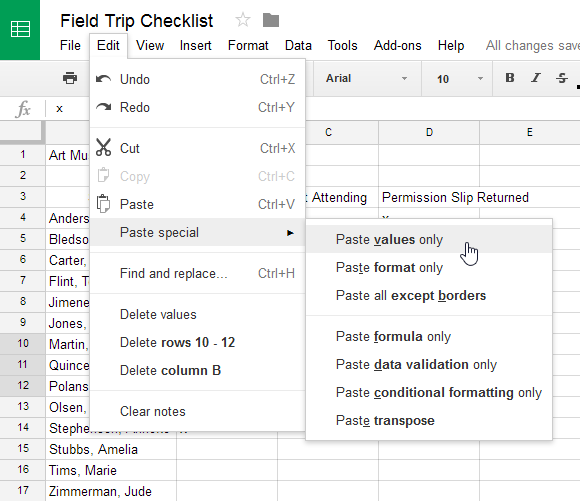
There may be times when you want to copy and paste only certain parts of a cell's content. In these cases, you can use the Paste Special option. Click Edit in the toolbar menu, hover the mouse over Paste Special, and select your desired paste option from the drop-down menu.
Rather than cutting and pasting, you can drag and drop cells to move their contents.
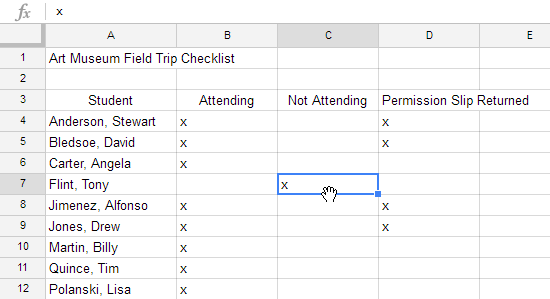
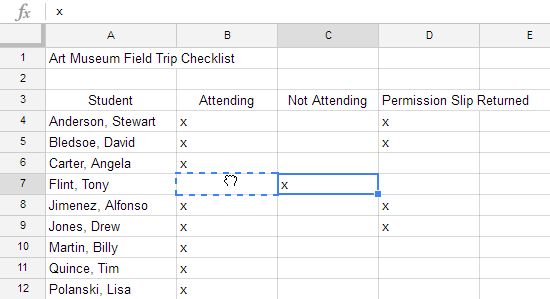
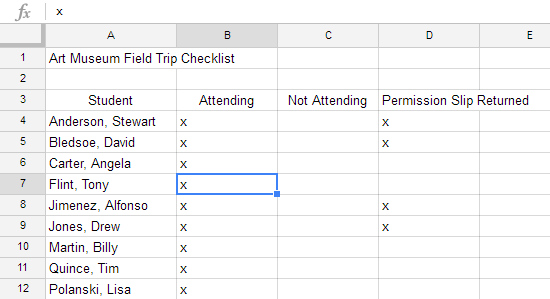
There may be times when you want to copy the content of one cell to several other cells in your spreadsheet. You could copy and paste the content into each cell, but this method would be time consuming. Instead, you can use the fill handle to quickly copy and paste content from one cell to any other cells in the same row or column.
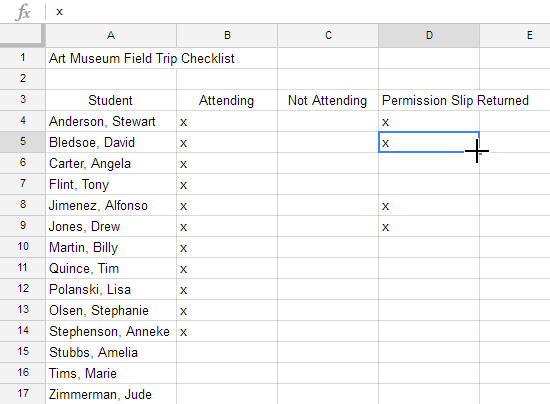

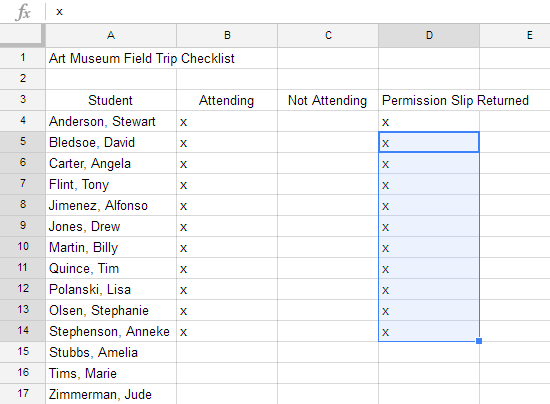
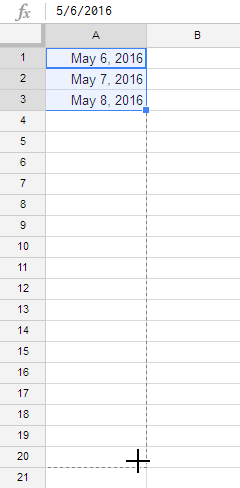
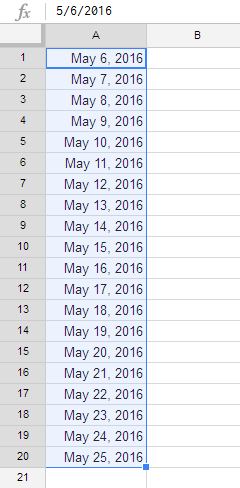
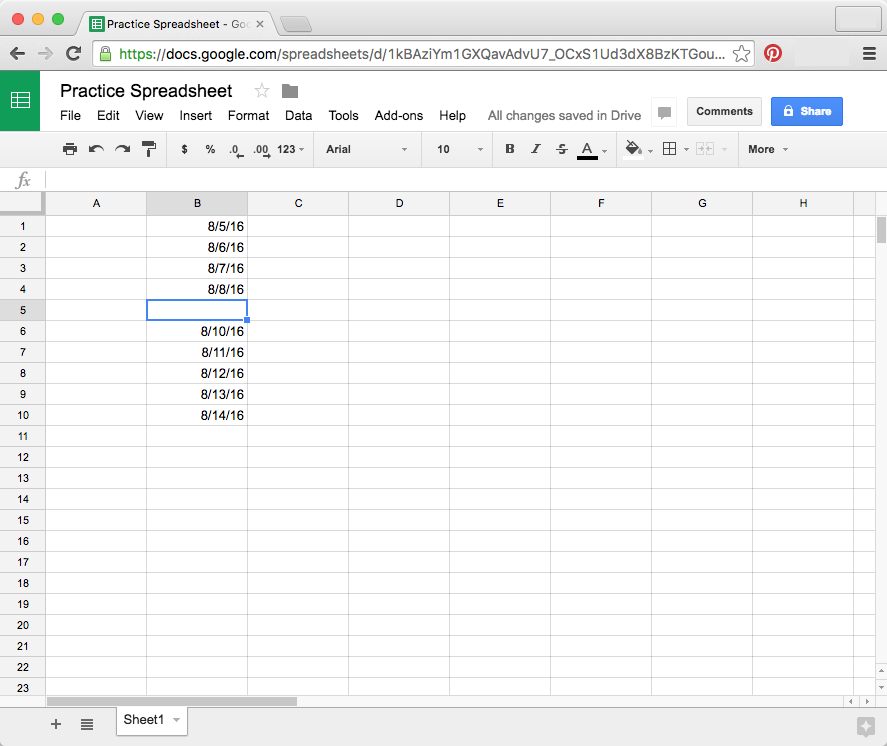
The fill handle can also be used to continue a series. Whenever the content of a row or column follows a sequential order—like numbers (1, 2, 3) or days (Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday)—the fill handle will guess what should come next in the series. In our example below, the fill handle is used to extend a series of dates in a column.
/en/googlespreadsheets/modifying-columns-rows-and-cells/content/