Portal:Sierra Leone
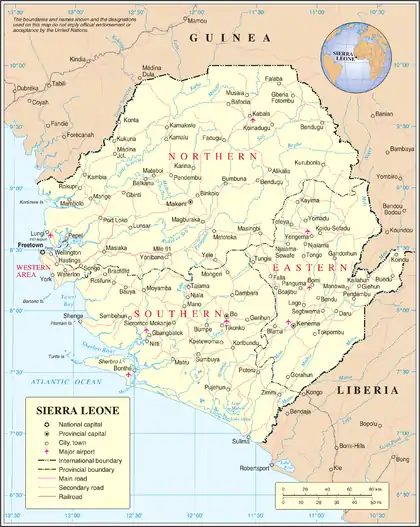
The Sierra Leone Portal Location of Sierra Leone Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It shares its southeastern border with Liberia, and the northern half is surrounded by Guinea. Covering a total area of 71,740 km2 (27,699 sq mi), it has a tropical climate, with environments ranging from savanna to rainforests. It has a population of 7,092,113 as of the 2015 census. Freetown is the capital and largest city. The country is divided into five administrative regions, which are subdivided into 16 districts. It is a constitutional republic with a unicameral parliament and a directly elected president serving a five-year term with a maximum of two terms. It is a secular nation with the constitution providing for the separation of state and religion and freedom of conscience (which includes freedom of thoughts and religion). Muslims make up about three-quarters of the population, with a Christian minority. Sierra Leone, as the country and its borders are known, was founded by the British Crown in two phases: first, the coastal Sierra Leone Colony in 1808 (for returning Africans after the abolition of slavery); second, the inland Protectorate in 1896 (as the Crown needed to establish more dominion inland following the outcome of the Berlin Conference of 1884–1885). Hence, it formally became known as the Sierra Leone Colony and Protectorate or simply British Sierra Leone. It gained independence from the United Kingdom on 27 April 1961, and became a Commonwealth realm on the same day; its name changed to the Dominion of Sierra Leone. Sir Milton Margai became its first prime minister. During decades following independence, Sierra Leone witnessed an increase in political activities, transformations, turmoil, humanitarian and socio-economic crises. It had its first general elections as an independent nation on 27 May 1961. Margai's Sierra Leone People's Party (SLPP) won a plurality of parliamentary seats and he was re-elected Prime Minister. A new constitution was adopted in 1971, paving the way for Sierra Leone becoming a republic, and Siaka Stevens, leader of the All People's Congress (APC), becoming the first executive president of the Republic of Sierra Leone. Stevens held on to this position for 14 years (until 1985) under a one-party system of government facilitated by the 1978 Constitution. Stevens' hand-picked successor Joseph Saidu Momoh promised to return the country to a multi-party system; a constitution was adopted in 1991 that provided the means for a multi-party democracy. A civil war broke out the same year, which went on for 11 years. In 1992, President Momoh was ousted in a coup led by Sierra Leone Army captain Valentine Strasser. Strasser was later ousted by his army colleague and second-in-command Julius Maada Bio, for failing to commit to a quick transfer to civilian rule. Bio would then return the country back to a democratic republic in 1996 through a general election. In 1996, the prospect of a transformation back to a multi-party democracy emerged, with the national debate "Peace before Elections vs Elections before Peace". Eventually, "Elections before Peace" won the debate. Ahmad Tejan Kabbah won the 1996 presidential election and became the first multi-party democratically elected president of Sierra Leone. Kabbah's presidency included a focus on fostering national unity and reconciliation, trust in government, peace and stability, the improvement in relations with countries, and the refounding of the Sierra Leone Armed Forces with special assistance and training led by the Government of the United Kingdom. About 18 ethnic groups inhabit Sierra Leone; the two largest are Temne and Mende peoples. About 2% of the country's population are Creole people, descendants of freed African-American and Afro-Caribbean slaves. English is the official language used in schools and government administration. Krio is spoken by 97% of the country's population. Sierra Leone has diamond, gold, bauxite and aluminium. It is a member of the United Nations, African Union, Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), Mano River Union, Commonwealth of Nations, IMF, World Bank, WTO, African Development Bank, and Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. It is home to Sub-Saharan Africa's first Western-style university: Fourah Bay College (established in 1827). (Full article...) Selected article -
An Ebola virus epidemic in Sierra Leone occurred in 2014, along with the neighbouring countries of Guinea and Liberia. On 18 March 2014, Guinean health officials announced the outbreak of a mysterious hemorrhagic fever "which strikes like lightning". It was identified as Ebola virus disease and spread to Sierra Leone by May 2014. The disease was thought to have originated when a child from a bat-hunting family contracted the disease in Guinea in December 2013. At the time it was discovered, it was thought that Ebola virus was not endemic to Sierra Leone or to the West African region and that the epidemic represented the first time the virus was discovered there. However, some samples taken for Lassa fever testing turned out to be Ebola virus disease when re-tested for Ebola in 2014, showing that Ebola had been in Sierra Leone as early as 2006. (Full article...)General images -The following are images from various Sierra Leone-related articles on Wikipedia.
| ||||
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
-
 List of all portalsList of all portals
List of all portalsList of all portals -
 The arts portal
The arts portal -
 Biography portal
Biography portal -
 Current events portal
Current events portal -
 Geography portal
Geography portal -
 History portal
History portal -
 Mathematics portal
Mathematics portal -
 Science portal
Science portal -
 Society portal
Society portal -
 Technology portal
Technology portal -
 Random portalRandom portal
Random portalRandom portal -
 WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
WikiProject PortalsWikiProject Portals
















.jpg.webp)














.svg.png.webp)


