Synthography
Synthography[1] is the method of generating digital media synthetically using machine learning. This is distinct from other graphic creation and editing methods in that synthography uses artificial intelligence art text-to-image models to generate synthetic media. It is commonly achieved by prompt engineering text descriptions as input to create or edit a desired image.[2][3]

Text-to-image models, algorithms, and software are tools used in synthography that are designed to have technical proficiency in creating the resulting artificial intelligence art output based on human input. Synthography typically uses text-to-image models to synthesize new images as a derivative of the training, validation, and test data sets on which the text-to-image models were trained.
Synthography is the method used, not the output itself. The output created specifically by generative machine learning models (as opposed to the broader category of artificial intelligence art) are referred to as synthographs.[1] Those who practice synthography are referred to as synthographers.[4][5] A synthographer can harness the ability of linguistic composition to tame a generative model. Other cases also include fine-tuning a model on a dataset to expand its creation possibilities.
Practical uses of synthography include AI-driven product shots, stock photography, and even magazine covers with some making predictions that synthography may be the future of photography.[6]
Etymology
From Latin synthesis "collection, composition", from Greek synthesis "composition, a putting together".[7]
"-graphy" is the word-forming element meaning "process of writing or recording" or "a writing, recording, or description" (in modern use especially in forming names of descriptive sciences). From French or German -graphie, from Greek -graphia "description of," used in abstract nouns from graphein earlier "to draw, represent by lines drawn," originally "to scrape, scratch" (on clay tablets with a stylus).[8]
Methodology
As synthography refers to the method of generating AI visuals, these are the mediums or classes used in the method.
| input \ output | text | image | 3D model | video |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| text | chatbot | text-to-image | text-to-3D | text-to-video |
| image | image-to-text | image-to-image | image-to-3D | image-to-video |
| video | video-to-video | |||
| brain | brain-to-image |
| white background | Doesn't exist yet |
| light green background | Currently exists in academia or beta |
| green background | Exists commercially or widely available |
(Note: text-to-speech and speech-to-text are purposely omitted in the table since that can simply be performed by dictation/transcription software and therefore is implied by the 'text' row and column. Also note that the mediums listed are of the class of medium, not specific instances of it ie: chatbot instead of ChatGPT.)
Difference between Synthography and Artificial Intelligence Art
Synthography is the method used to create synthetic media using generative models. Artificial intelligence art (including music, cooking, and video game level design) is the output created using artificial intelligence which is an overly and increasingly broad category.
When Elke Reinhuber coined the term synthography in her paper, "Synthography – An Invitation to Reconsider the Rapidly Changing Toolkit of Digital Image Creation", she spoke of a "legitimation crisis" as a need for the term. Before generative models were used, artificial intelligence art algorithms already existed in mediums such as graphics editing software (ie: content-aware fill, application of artistic styles, resolution enhancement) which employs a wide range of artificial intelligence tools, and DSLR and smartphone cameras (ie: object recognition, in-camera focus stacking, low-light machine learning algorithms) all of which continue to undergo rapid development.[1]
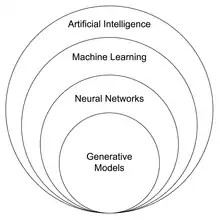
Artificial intelligence is a superset of Machine learning. Machine learning is a superset of neural networks. Neural networks are a superset of generative models such as GAN's (generative adversarial networks) and diffusion models. The relation between all of these is depicted in the Venn diagram shown here. Synthography specifically uses generative models, as popularized by software such as DALL-E, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion.
References
- Reinhuber, Elke (2 December 2021). "Synthography–An Invitation to Reconsider the Rapidly Changing Toolkit of Digital Image Creation as a New Genre Beyond Photography". Google Scholar. Retrieved 20 December 2022.
- Smith, Thomas (26 October 2022). "What is Synthography? An Interview With Mark Milstein - Synthetic Engineers". syntheticengineers.com. Synthetic Engineers. Retrieved 20 December 2022.
- Oosthuizen, Megan (20 December 2022). "Artist Shows Us What A Live-Action Movie Could Look Like". fortressofsolitude.co.za. Fortress Entertainment. Retrieved 10 February 2023.
- Ango, Stephan (3 July 2022). "A Camera for Ideas". stephanango.com. Retrieved 10 February 2023.
- Growcoot, Matt (17 March 2023). "AI Photographers or 'Synthographers'". petapixel.com. PetaPixel. Retrieved 25 March 2023.
- Katz, Neil (8 March 2023). "Synthography is the Future of Photography". thisismeteor.com. Meteor. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- "synthesis". etymonline.com. Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 27 December 2022.
- "-graphy". etymonline.com. Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 27 December 2022.
